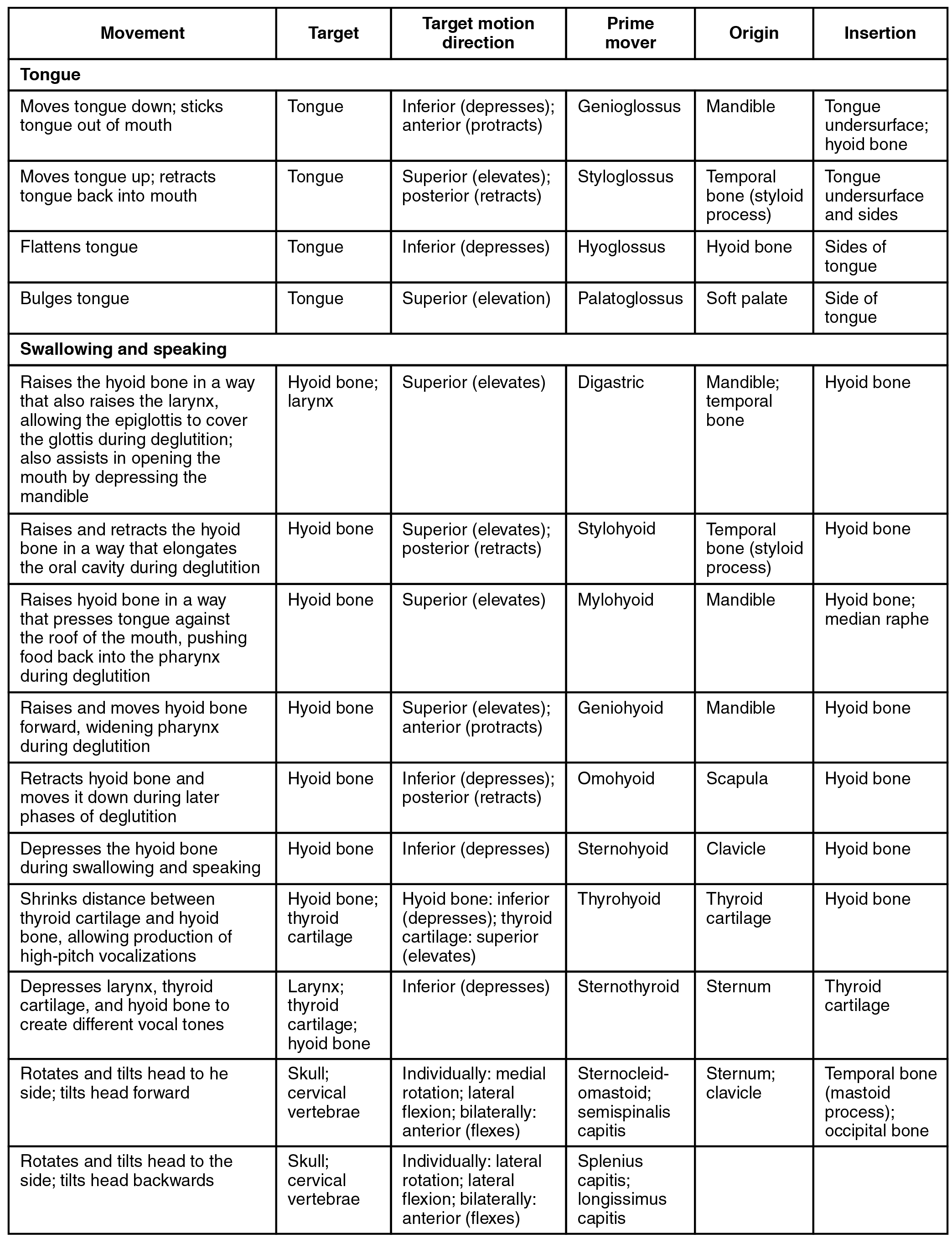
Muscles That Move the Head, 2 Trunk Muscles, 2 Muscles of the Thorax, 2 Muscles of the Abdominal Wall, 2 Muscles of the Back, 290 Muscles of the Pelvic Floor, 290 Upper Limb Muscles, 293 Muscles Acting on the Shoulder Girdle, 293 and most muscles funcLEVER SYSTEMS lever Anatomy of the Muscular System Chapter 10 D A, These muscles include the serratus posterior inferior and the serratus posterior superior Intrinsic muscles The intrinsic, or deep, muscles allow forHead hed 1 the anterior or superior part of a structure or organism 2 in vertebrates, the part of the body containing the brain and the organs of special sense Called also caput articular head an eminence on a bone by which it articulates with another bone head injury traumatic injury to the head resulting from a fall or violent blow Such an
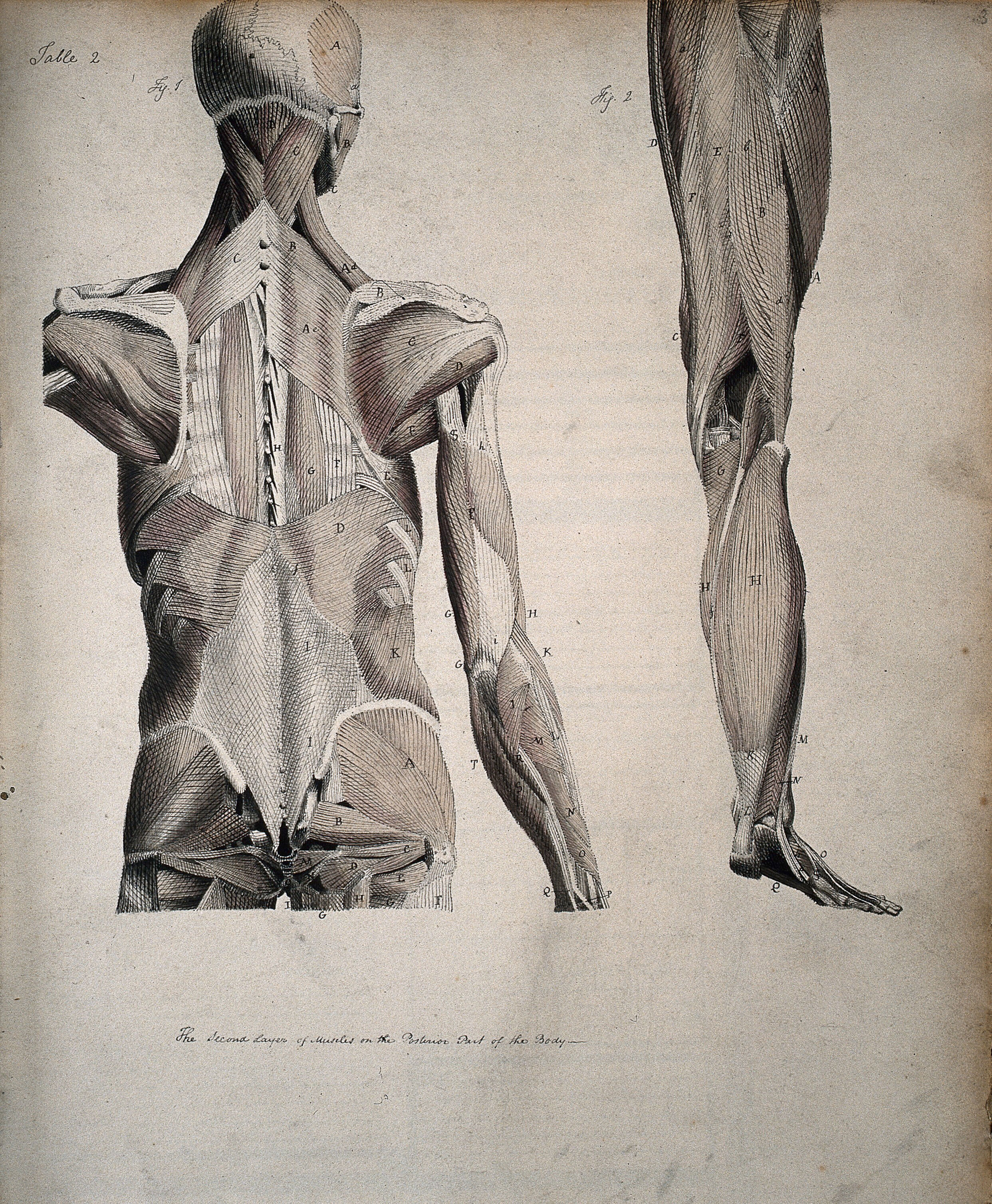
Left Muscles Of The Head And Trunk Back View Right Muscles Of The Thigh And Leg Back View Coloured Drawing 18 Wellcome Collection
Back of head muscle anatomy
Back of head muscle anatomy-This is the sneak peek at our full video tutorial about the main muscles of the head and neck You will learn about the most important muscles for facial expVimeo Player LocalStorage Proxy There is a dissection assistance pdf file that you can use to assist you in your lab preparation Category Back & Spine, Back & Spine, Back & Spine, Human Dissection Labs, Human Dissection Labs, PreClinical, PreMedical, Regional Anatomy s back dissection, cranial neve 11, dissection, latisumus dorsi
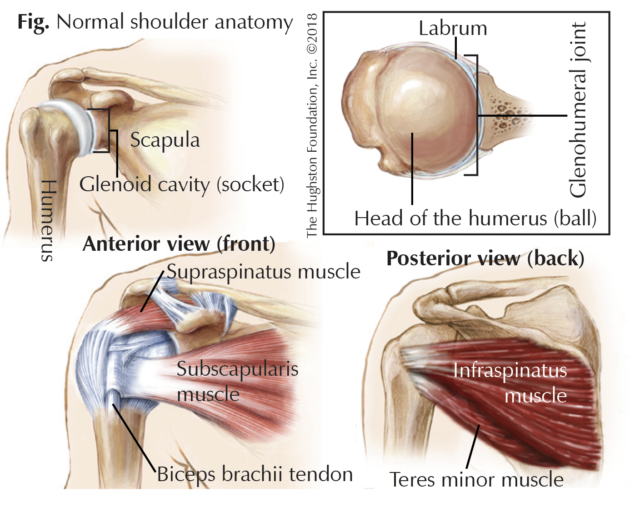



Swimmer S Shoulder Hughston Clinic
Learn more about how different organs look and work Learn more about the hardest working muscle in the body with this quick guide to the anatomy of the heart Organs are the body's vital structures, using complex structures to perform specialized tasks anatomy of back organs An autotroph is an organism that can make its own food for energyThe longissimus (red, in the image above) are located between spinalis and the iliocostalis muscles There are three sets of longissimus muscles 1) above the cervical area (longissimus capitis), 2) in the cervical area (longissimus cervicis), and 3) in theThe shoulder muscles play a large role in how we perform tasks and activities in daily life The anatomy of the sartorius muscle of your thigh Learn how they work and how to exercise them Trapezius muscles are the site of many a sore spot Paraspinal muscles are those long back muscles that sometimes get ropy
Muscles of the Neck Neck Anatomy Muscles Pictures There are many muscles around the neck that help to support the cervical spine and allow you to move your head in different directions Here is a list of the many muscles that exist in the neck Longus Colli & Capitis – Responsible for flexion of the head and neck Head and neck anatomy is important when considering pathology affecting the same area In radiology, the 'head and neck' refers to all the anatomical structures in this region excluding the central nervous system, that is, the brain and spinal cord and their associated vascular structures and encasing membranes ie the meningesThe nuchal plane is rough and irregular to attach to several muscles, including the muscles of the head and neck The internal surface of the squamous part is bowlshaped and divided into four depressions of the cruciform eminence
The muscles of the chest and upper back occupy the thoracic region of the body inferior to the neck and superior to the abdominal region and include the muscles of the shoulders These important muscles control many motions that involve moving the arms and head — such as throwing a ball, looking up at the sky, and raising your hand The back contains the spinal cord and spinal column, as well as three different muscle groups As these muscles contract and relax, they move skeletal bones to create movement of the body The human body is fascinating to study, which is why anatomy is such a popular subject 13,276 anatomy of the head and neck stock photos, vectors, and illustrations are available royaltyfree See anatomy of the head and neck stock video clips of 133 muscle head anatomy vocal organ diagram female neck anatomy neck wireframe head neck human anatomy head artery anatomy face pharynx vector neck degree head anatomy 3d




Obliquus Capitis Inferior Muscle Wikipedia



Pearsonhighered Com
The Organs of the Head include the ear, the eye, the nose and sinuses, the salivary glands, and the oral cavity The ear can be divided in to three sections the external ear, the middle ear, and the inner earThe external ear functions to capture and direct sound waves through the external acoustic meatus to reach the tympanic membrane (ear drum) ) The tympanic membrane marksBrain Anatomy and How the Brain Works AKA the medial longitudinal fissure) that runs from the front of the head to the back The right hemisphere controls the left side of the body, and the left half controls the right side of the body The two halves communicate with one another through a large, Cshaped structure of white matter and nerve The muscles of the neck run from the base of the skull to the upper back and work together to bend the head and assist in breathing Learn more about skin anatomy at howstuffworks Stockbyte / getty images anatomical study of the skull is a worthwhile component of your figure drawing study



Muscles Of The Head And Neck Anatomy Pictures And Information




Muscle Of The Head And Neck Illustration Stock Image C039 1784 Science Photo Library
Official Ninja Nerd Website https//ninjanerdorgNinja Nerds!In this lecture Professor Zach Murphy will present on the muscles of the head & neck while usin3 rows Back muscles The back muscles are anatomically layered into superficial (extrinsic) andEqually important is the erector spinae muscles



Male Back Neck And Head Muscles Computer Illustration Anatomical 3d Model Stock Photo




Muscles Of The Neck And Torso Classic Human Anatomy In Motion The Artist S Guide To The Dynamics Of Figure Drawing
The deep muscles develop embryologically in the back, and are thus described as intrinsic muscles The superficial and intermediate muscles do not develop in the back, and are classified as extrinsic muscles This article is about the anatomy of the superficial back muscles – their attachments, innervations and functionsMuscles of the Head and Neck Humans have welldeveloped muscles in the face that permit a large variety of facial expressions Because the muscles are used to show surprise, disgust, anger, fear, and other emotions, they are an important means of nonverbal communication Muscles of facial expression include frontalis, orbicularis oris, laris oculi, buccinator, and zygomaticusThese musclesThe large, complex muscles of the neck and back move the head, shoulders, and vertebral column The erector spinae group forms the majority of the muscle mass of the back and it is the primary extensor of the vertebral column




Human Torso Skeleton With Muscles Veins And Arteries Back View Human Anatomy Torso Skeleton With Muscles Veins And Canstock




Labeled Anatomy Chart Of Neck And Back Muscles On White Background Stock Photo Alamy
Usually, headaches in the back of head are the result of stress, muscle tightness, tension, the overuse of medications, and tiredness Sometimes a pain in the base of your skull can be caused by Occipital neuralgia which is a condition that affects the nerves that run from the top of the spinal cord up through the scalpThe top section of the spine is the cervical section, which contains nerves that innervate muscles of the head, neck and thoracic cavity, as well as transmit sensory information to the CNS The cervical spine section contains seven vertebrae, C1 through C7, and eight nerve pairs, C1 through C8Together, these muscles bring the head into an upright position



Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And Physiology



Neck Muscles And Other Soft Tissues
The anatomy of the head and neck of the human body, including the bones, muscles, blood vessels, nerves, glands, nose, mouth, and throat Head & Neck Anatomy 19 3D model by INTERVOKE (@intervoke)3d illustration of female head muscles anatomy with front back and side view Infraspinatus muscle Trigger points and pain in the arm and shoulder blade The deep muscles of the arm Vector image More similar stock illustrations Human anatomy full body muscles The three deep muscles of the back include the semispinalis, multifidus, and rotatores These muscles stabilize the vertebral column and also have a role in proprioception and balance Moreover, these muscles help with the movements of




Occipital Neuralgia And Suboccipital Headache C2 Neuralgia Treatments Without Nerve Block Or Surgery Caring Medical Florida




Female Head Muscles Anatomy Back View Stock Illustration
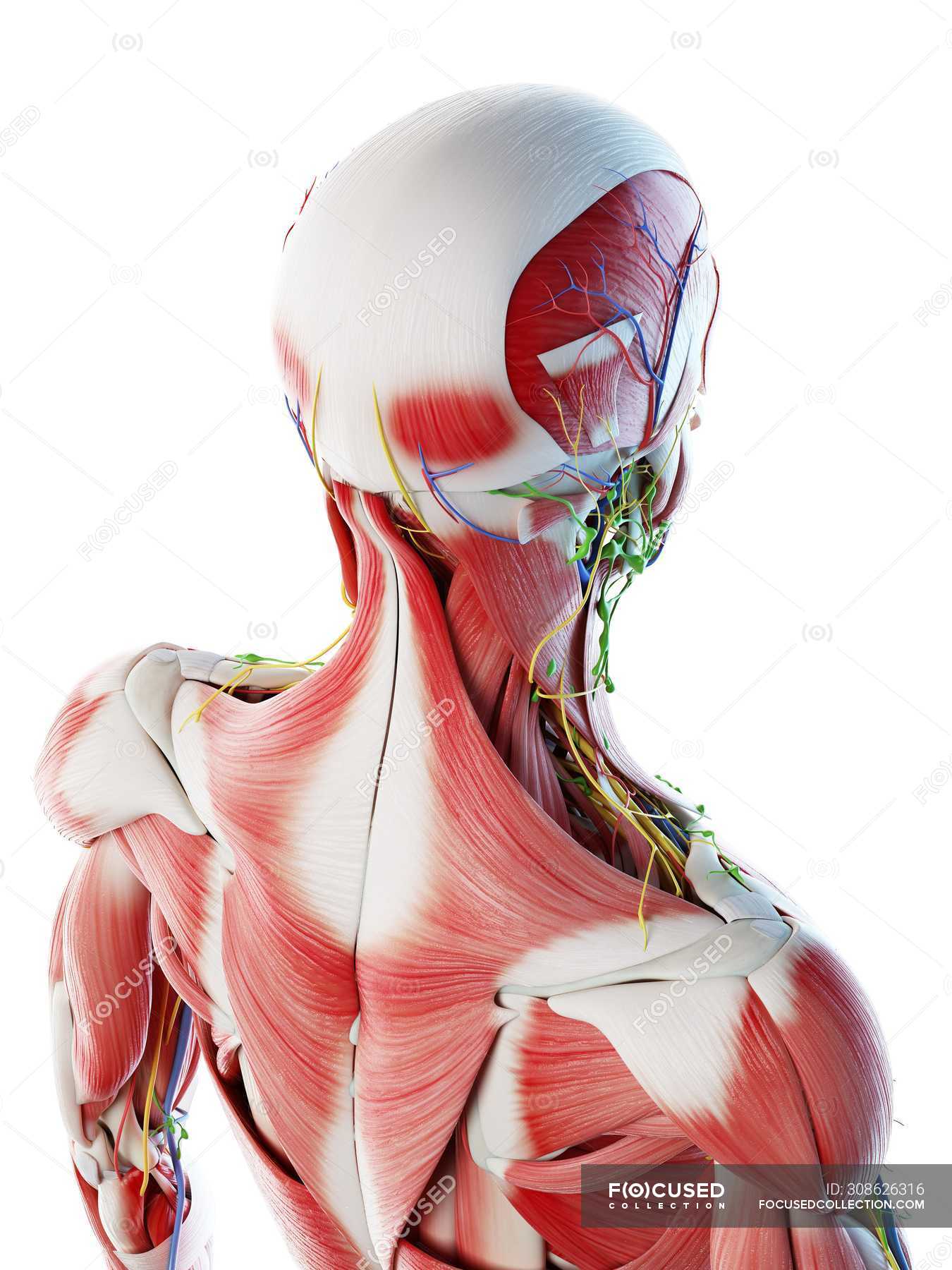
The two trapezius muscles together form a kite shape The trapezius muscle can be involved in extending the head upward or neck backward, rotating/turning the head, or lifting the shoulder blade See Thoracic Spine Anatomy and Upper Back Pain; Sternocleidomastoid This large neck muscle helps rotate the head upward and side to side The muscles of the face overlap and crisscross over each other, creating a mask of muscleThe trapezius is a large surface muscle that spans from the base of the skull down the spine to the mid back, as well as out to the shoulder blade The trapezius muscle has 3 parts upper, middle, and lower It can help extend the head upward and neck backward, rotating/turning the head, or lifting and/or depressing the shoulder blade



Head Muscles Photograph By Asklepios Medical Atlas



Labeled Anatomy Chart Of Male Back Muscles On Black Background Wall Mural Hank Grebe
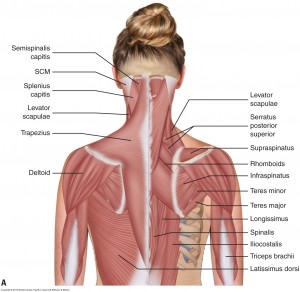
Erector spinae Numerous muscles comprise the erector spinae muscles throughout the spineThe splenius capitis muscle is a broad, strap like muscle located in the back of the neck It connects the base of the skull to the vertebrae in the neck and upper thorax When one muscle acts singly, it causes the head to rotate and bend toward one side;Four muscles, arising from the palmar surface of the shafts of metacarpals 1, 2, 4, & 5 (the 1st palmar interosseous is often fused with the adductor pollicis m) base of the proximal phalanx and extensor expansion of the medial side of digits 1 & 2, and lateral side of digits 4 & 5
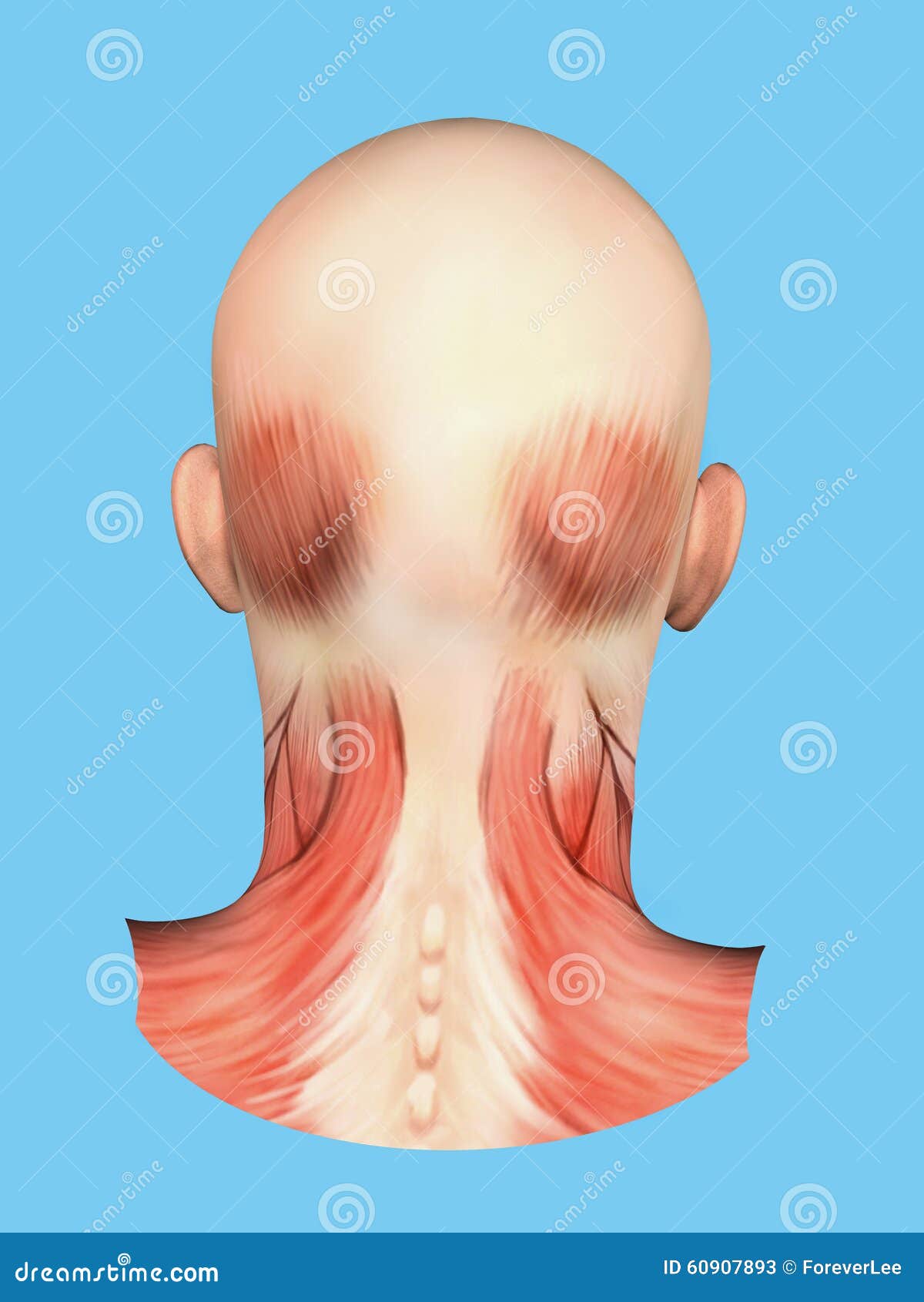



Anatomy Of Muscles On Back Of Head Stock Illustration Illustration Of Sternocleidomastoid Anatomy
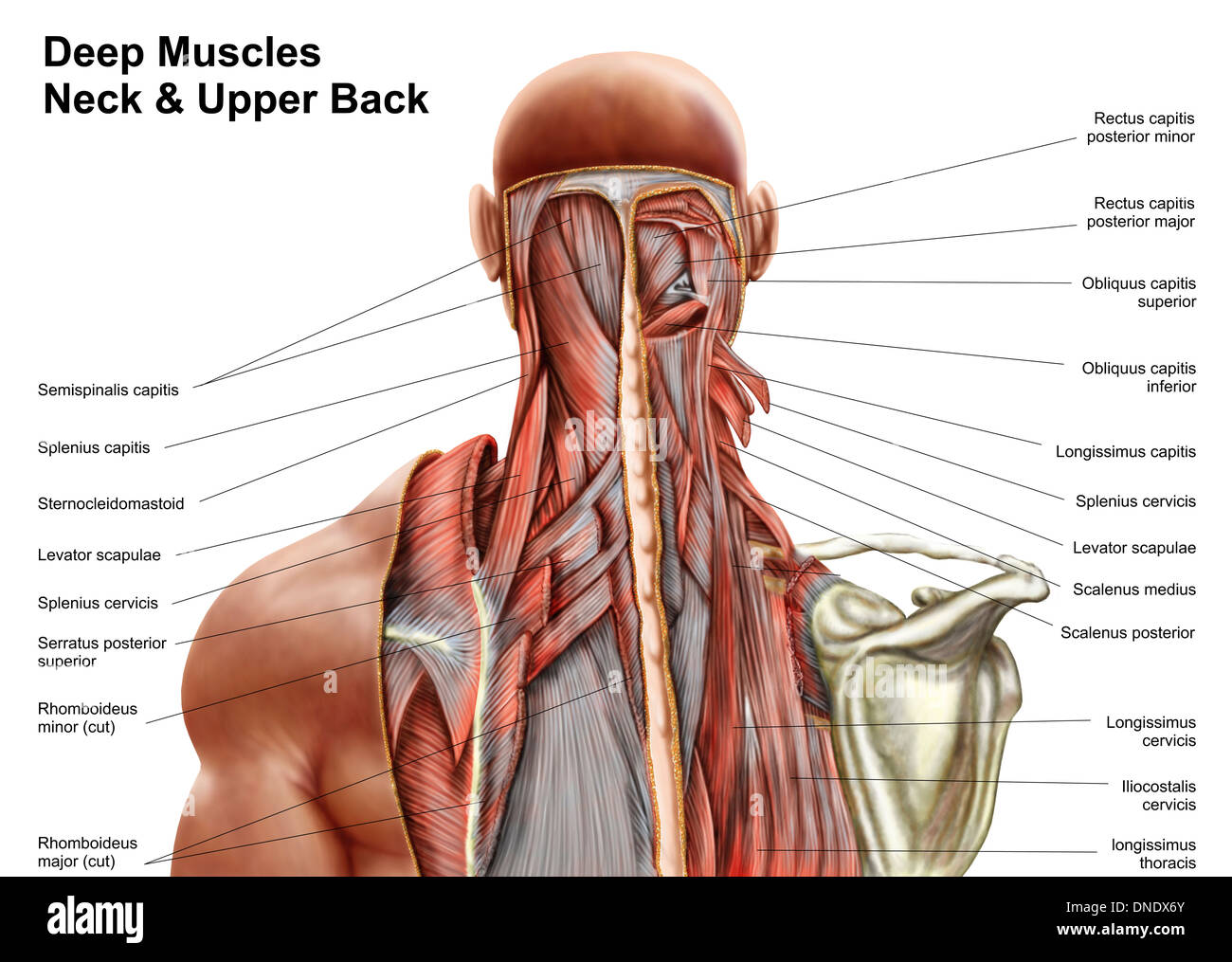



Human Anatomy Showing Deep Muscles In The Neck And Upper Back Stock Photo Alamy
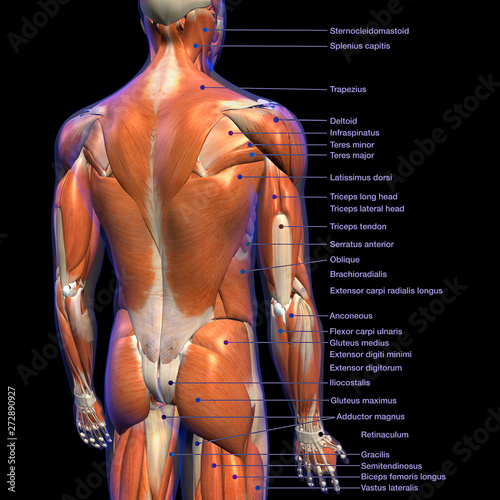
The neck muscles, including the sternocleidomastoid and the trapezius, are responsible for the gross motor movement in the muscular system of the head and neck They move the head in every direction, pulling the skull and jaw towards the shoulders, spine, and scapulaMuscle Back Of Head Anatomy Anatomy Massage Therapy Migraine / Admin Sabtu, 25 September 21 Head impacts increase the risk for concussio We appreciate your review of the support network In general, muscles work when calcium ions are released, which triggers muscle cells to contract Whether they come at night or during the day, cramps Back Anatomy All About the Back Muscles The back anatomy includes the latissimus dorsi, trapezius, erector spinae, rhomboid, and the teres major On this page, you'll learn about each of these muscles, their locations and functional anatomy Contents hide Function of the Back Muscles Latissimus Dorsi (Lats)




Cervical Dysfunction And Pain In The Head And Neck Causes And Osteopathic Options
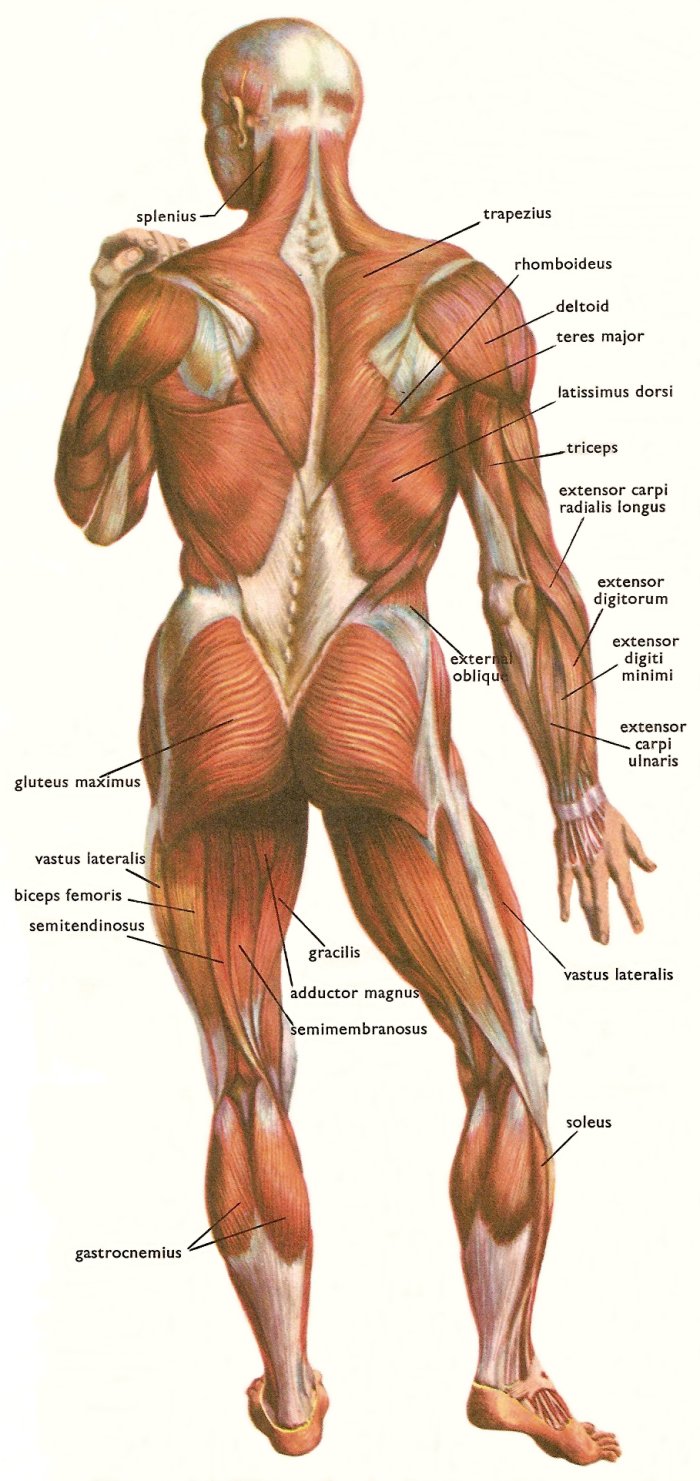



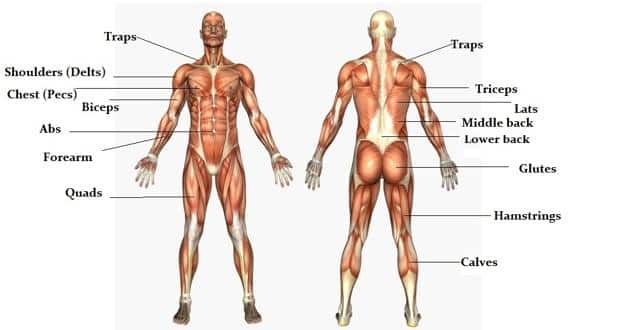
Skeletal Muscles And Muscle Groups
Human Anatomy Muscles back of the head and the neck So many muscles that cause migraines, arm, neck, shoulders, and back pain Human Anatomy Muscles back of the head and the neck Today Explore When autocomplete results are available use up and down arrows to review and enter to select Touch device usersThe muscles of the back and neck are responsible for maintaining posture and facilitating movement of the head and neck They are divided into three layers Superficial Layer Two muscles in the superficial layer are responsible for rotation of the head Splenius Capitis A thick rectangular muscle, the most superior of the neck muscles Human head (anterior view) The human head is more than just a nuisance responsible for your headaches It is a complex anatomical structure weighing up to five kilograms that rests on the bony skull and in turn, the neckIn addition to the evident ears, eyes, nose, and mouth, the head supports a variety of other important structures Muscles of mastication
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/male-musculature--artwork-147218800-cb22d819dc434b75bb6f4bf020e9ed8c.jpg)



Sternocleidomastoid Muscle Anatomy And Function




Head And Neck Anatomy
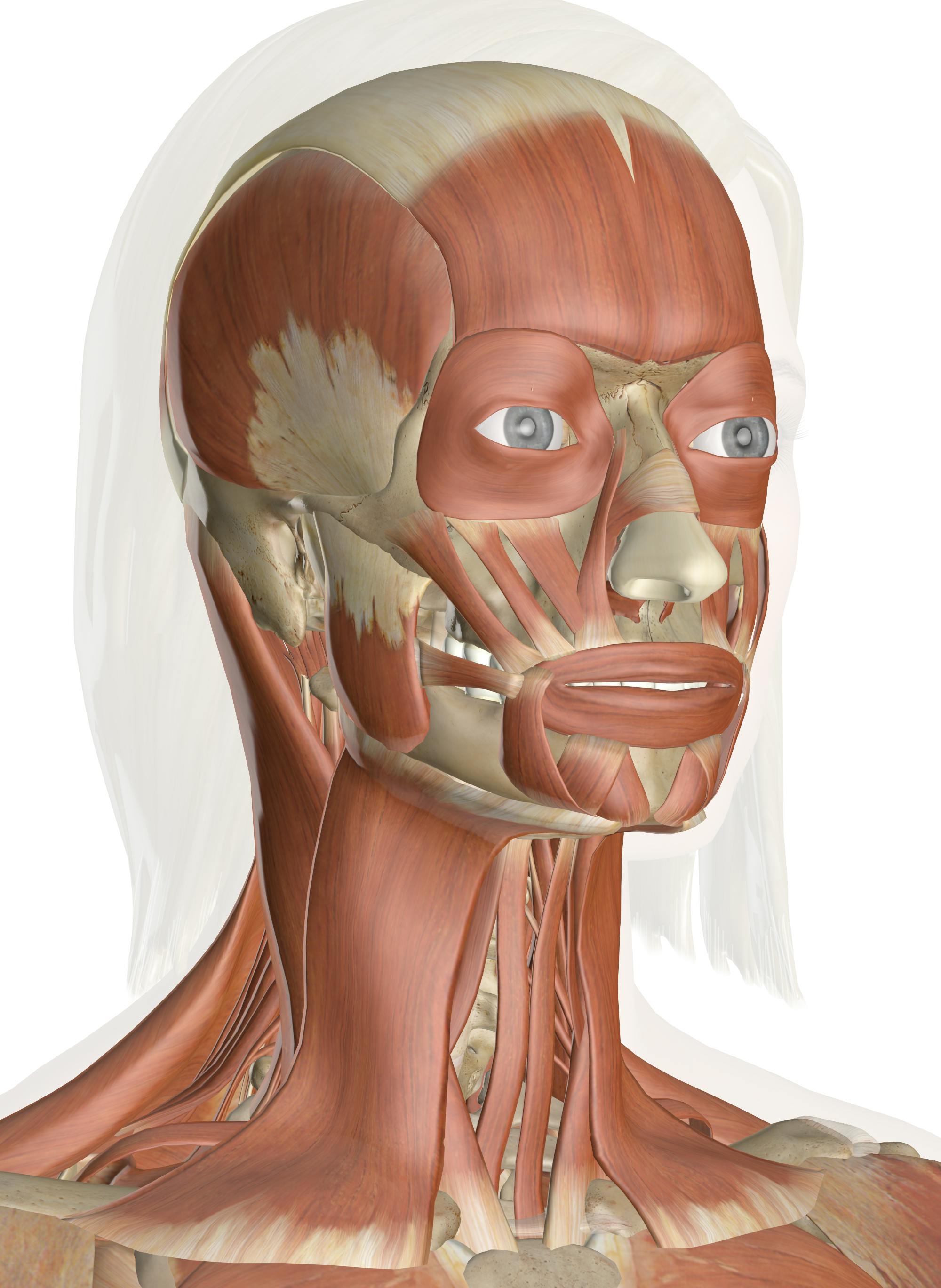
Neck muscles are bodies of tissue that produce motion in the neck when stimulated The muscles of the neck run from the base of the skull to the upper back and work together toBack Muscles Attachments, Nerve Supply & Action Back Muscles The muscles of the back that work together to support the spine, help keep the body upright and allow twist and bend in many directions The back muscles can be three types a Superficial Back Muscles b Intermediate Back Muscles and Movements of the shoulderHead Muscles Anatomy By Stepan Ayvazyan The muscles of the head are divided into two large groups – the mimic muscles and the muscles of mastication The main functions of the mimic muscles are the transmission of emotions through facial expressions, as well as participation in defensive reactions, such as blinking or sneezing
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/10606/Head_Thumbnail__1_.png)



Head Anatomy Muscles Glands Arteries And Nerves Kenhub
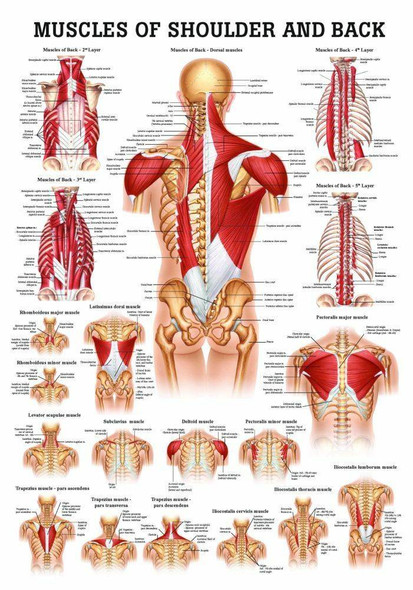



Muscles Of The Abdomen And Ribs Laminated Anatomy Chart
Related Posts of "Muscle Anatomy Back Of Neck" Muscle Anatomy Diagram Printable Muscle Anatomy Diagram Printable 12 photos of the "Muscle Anatomy Diagram Printable" muscle anatomy diagram printable, Human Muscles, muscle anatomy diagram printable Head And Neck Muscle Anatomy Back Of Neck Anatomy Diagram / Human Head Back Side Female Head Muscles Anatomy Back View The neck also protects the nerves and the spinal cord as well to help maintain a healthy neck anatomy area diagram body maps Find out more about your back here!Anatomy and physiology is a course that builds on the material from the previous chapters, so if you learn the meaning of terms like superior or inferior early in the semester, then you'll understand intuitively that the superior vena cava is going to be above the inferior vena cava in the heart In addition, you'll probably by using these directional terms often when you're documenting
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12060/Img.jpg)



Anatomy Of The Back Spine And Back Muscles Kenhub




What Muscles Cause Neck And Head Pain Physit
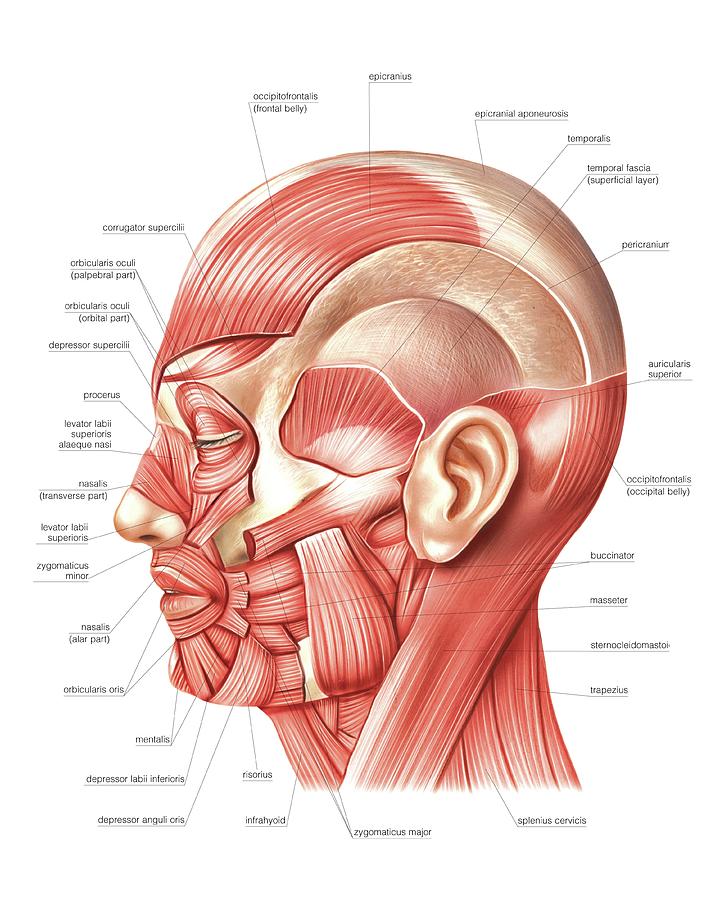
In other words, there is a muscle on the forehead (frontalis) and one on the back of the head (occipitalis), but there is no muscle across the top of the head Instead, the two bellies are connected by a broad tendon called the epicranial aponeurosis , or galea aponeurosis (galea =Anatomy & Physiology Muscles A flat, thing muscle in the wall of the cheek a broad sheet of muscle fibers extending from the collarbone to the angle of the jaw each of a pair of long muscles that connect the sternum, clavicle, and mastoid process of the temporal bone and serve to turn and nod the headIn this video lesson, you will discover the main muscles of the head, neck and shoulders Muscles of the Head The forehead is covered by a flat and wide muscle, called the frontalis In fact, it is the front portion of quite a large muscle that covers the entire top and back section of the skull




Pin On Anatomy




Human Back Human Head Human Body Muscle Others Head Human Anatomy Png Pngwing




Trapezius Physiopedia




Levator Scapulae Muscles In Isolation Rear View Of Upper Back Papier Peint Papiers Peints Tete Crane Col De L Uterus Myloview Fr




Posterior Triangle Of The Neck Head And Neck Anatomy Muscle Human Body Latissimus Dorsi Hand Human Head Png Pngwing




Head And Neck Human Anatomy Muscles




Left Muscles Of The Head And Trunk Back View Right Muscles Of The Thigh And Leg Back View Coloured Drawing 18 Wellcome Collection




Swimmer S Shoulder Hughston Clinic
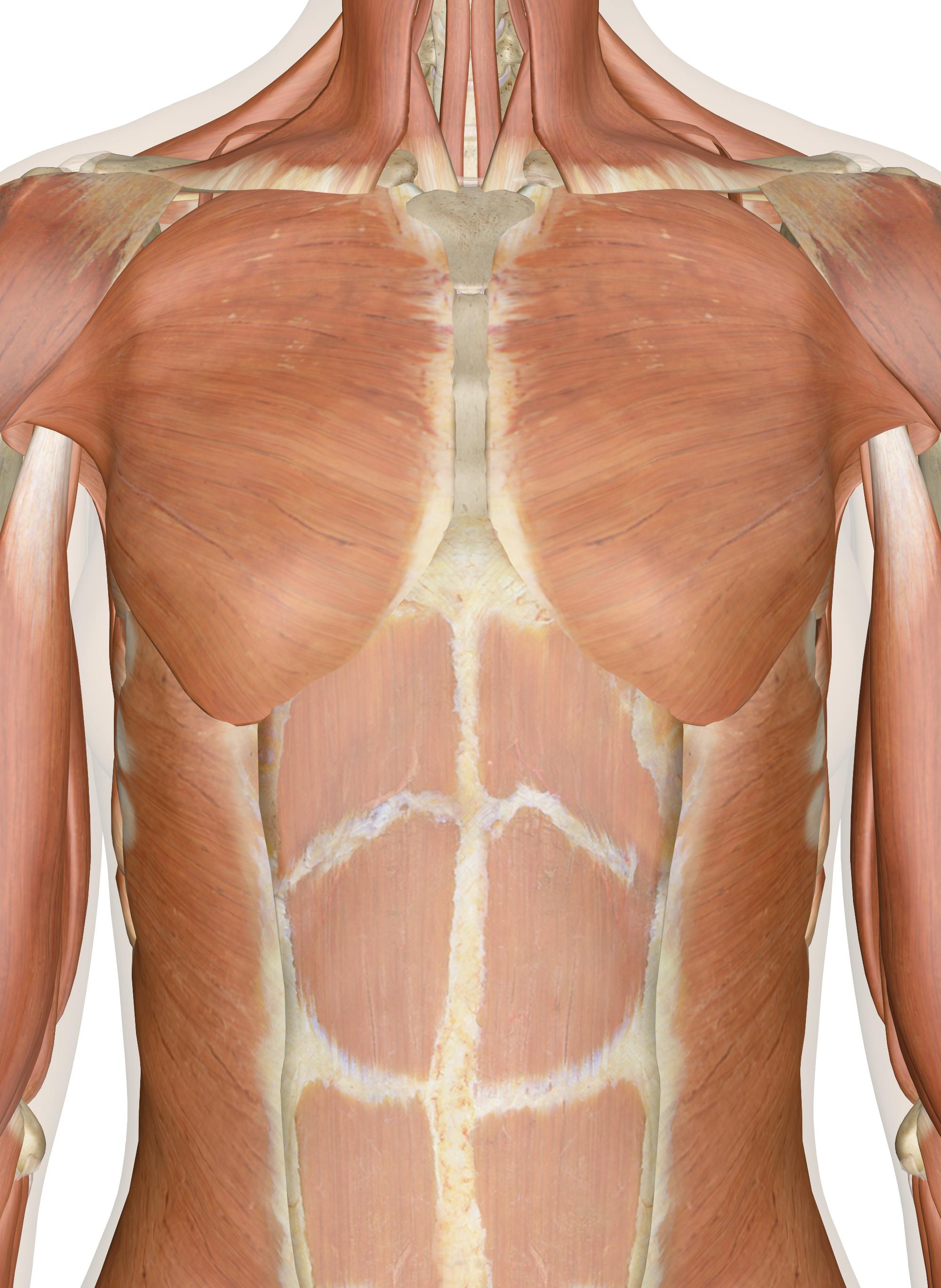



Muscles Of The Chest And Upper Back
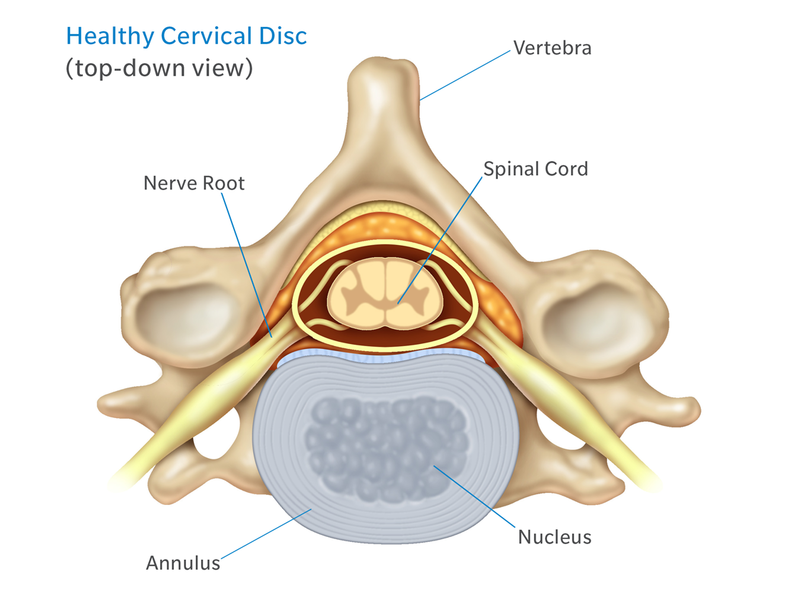



Anatomy Of The Neck Causes Of Neck Pain And How To Manage The Pain



3d Anatomy Illustration Of Human Head With Skull Royalty Free Image Panthermedia Stock Agency



The 6 Best Muscles To Self Massage For Instant Relief Of Neck And Upper Back Tension Head To Toe Muscle Clinic




11 3 Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Douglas College Human Anatomy And Physiology I 1st Ed



Muscle Anatomy




Lecture Notes In Dentistry Lecture Notes For Muscles Of The Head And Neck Head Muscles Neck Muscle Anatomy Muscle Diagram




File 1117 Muscles Of The Neck And Back Jpg Wikimedia Commons



Shoulder Pain And Common Shoulder Problems Orthoinfo os




Medical 3d Illustration Of The Head Muscles Canstock




Muscular Anatomy And Soft Tissue Headandcervicalspine
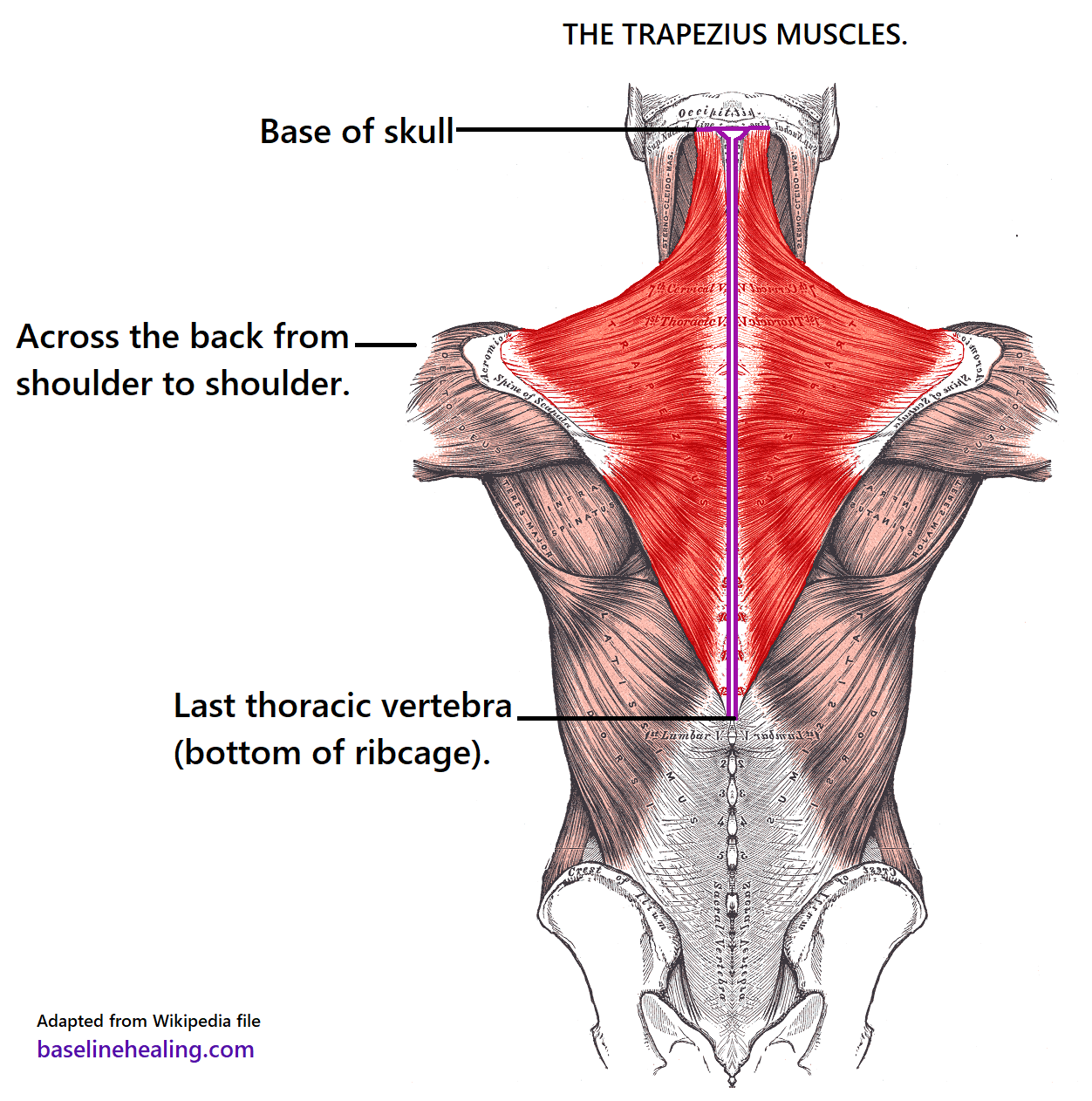



Trapezius Muscles Anatomy Attachments In Detail




Left Muscles Of The Head And Trunk Back View Right Muscles Of The Thigh And Leg Back View Coloured Drawing 18 Wellcome Collection




Facial Muscles And Expressions Classic Human Anatomy In Motion The Artist S Guide To The Dynamics Of Figure Drawing



Neck Muscles Pain




Muscles Of The Neck And Head Rear Spc Id 2106 Science 3d Illustration
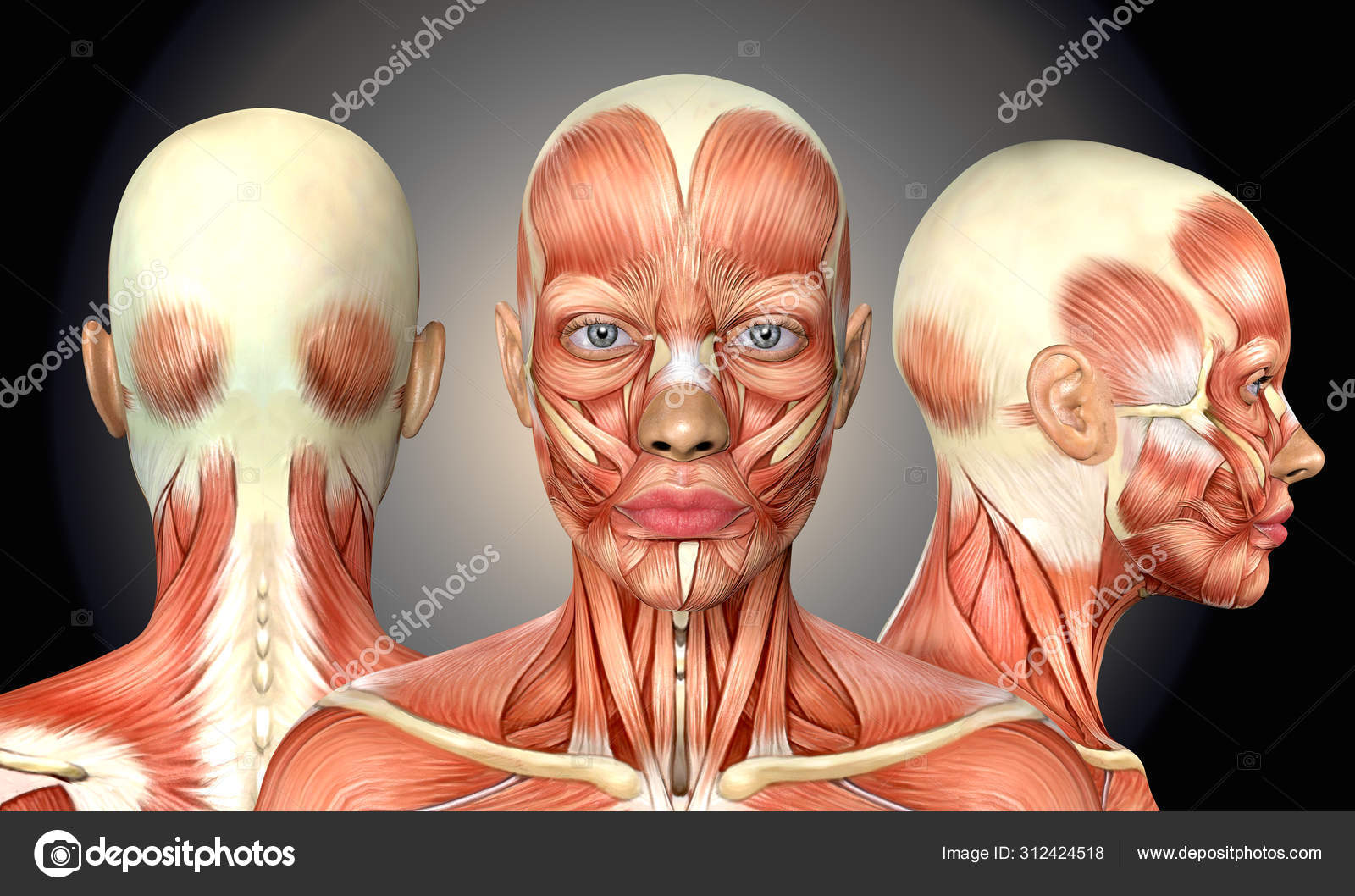



3d Illustration Of Female Head Muscles Anatomy With Front Back A Stock Photo By C Deryadraws



The Massive Muscle Anatomy And Body Building Guide You Always Wanted Thehealthsite Com



Understanding Chronic Headaches And Fighting The Pain




Spinal Muscles A Comprehensive Guide
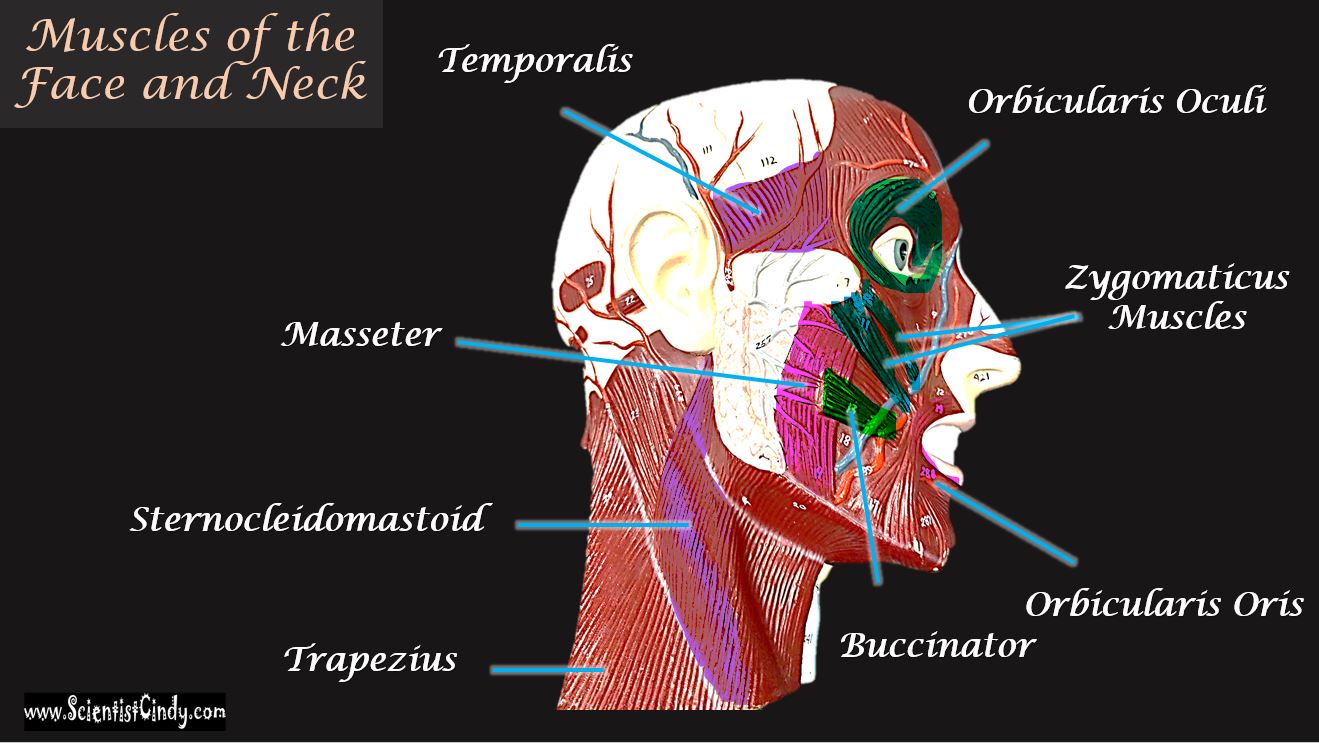



The Muscles Of The Head Trunk And Shoulders Scientist Cindy




51 309 Back Muscles Stock Photos And Images 123rf
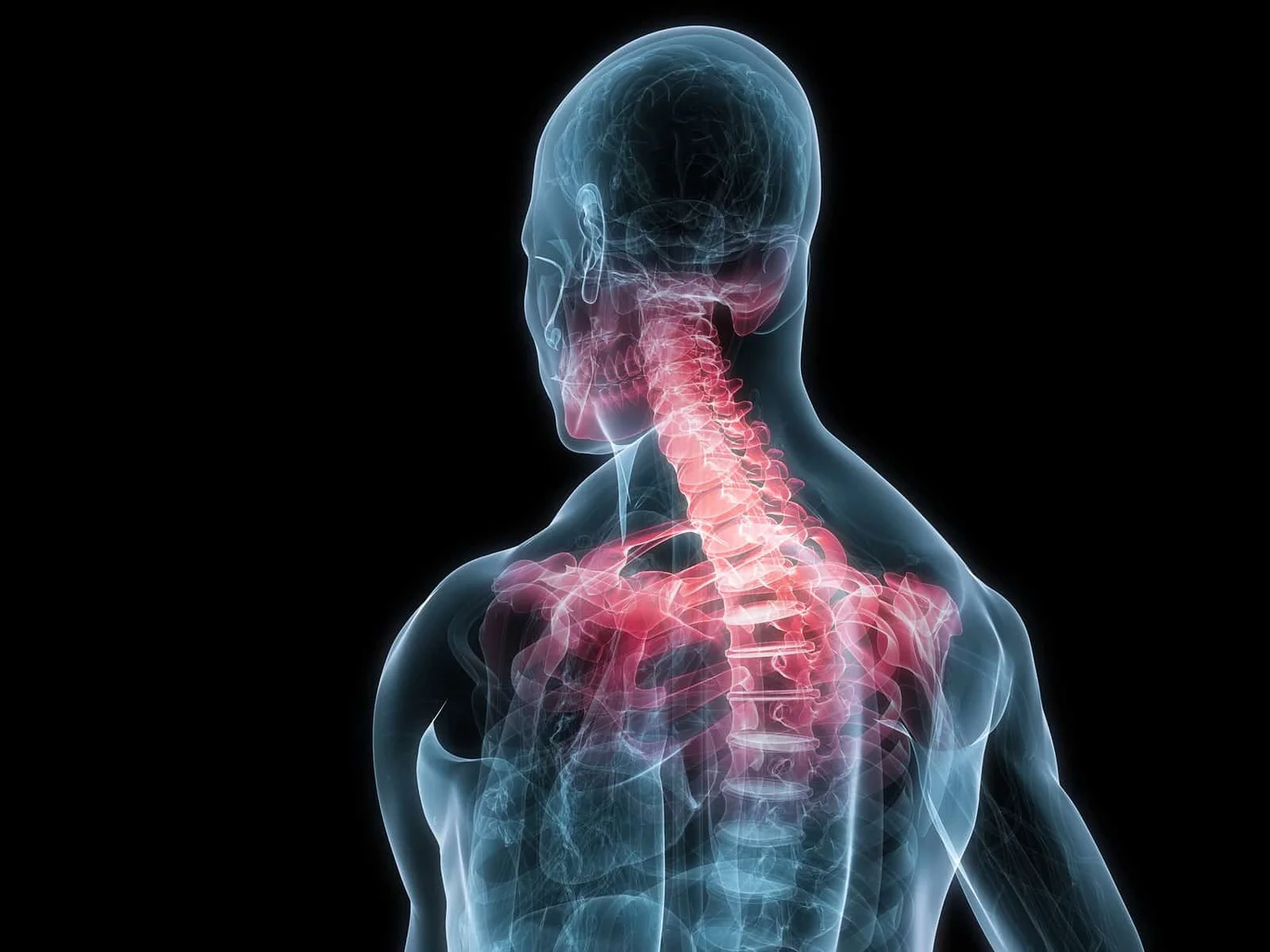



The Link Between Posture And Chronic Neck And Upper Back Pain Back Pain And Headache Specialist Burke Va Nova Headache Chiropractic Center
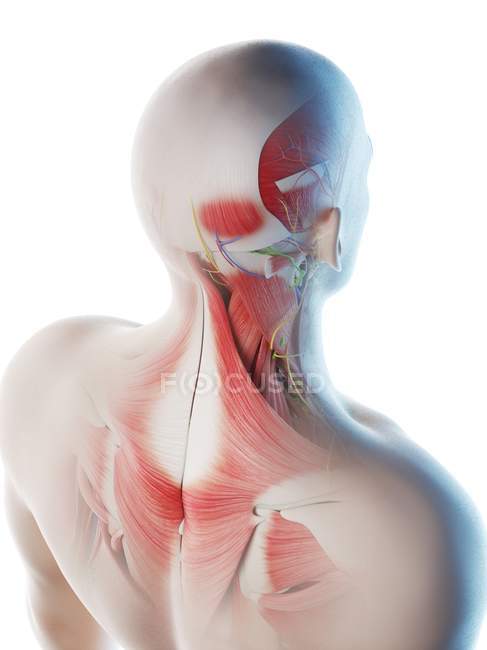



Male Back Neck And Head Muscles Computer Illustration 3d Artwork Stock Photo



1




Anatomy Anatomy Massage Therapy Migraine
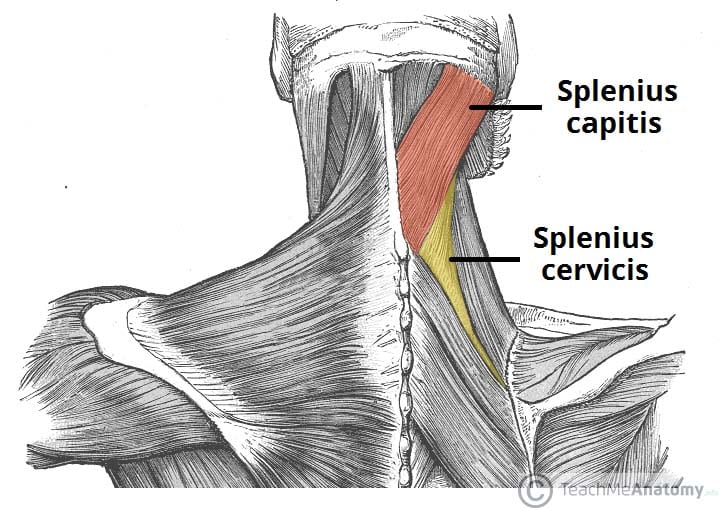



The Intrinsic Back Muscles Attachments Actions Teachmeanatomy
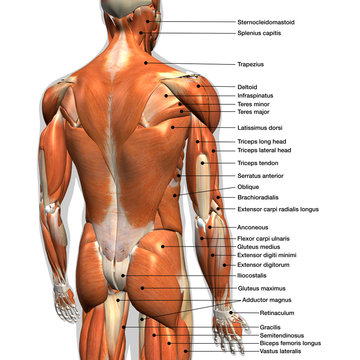



17 519 Best Back Muscles Anatomy Images Stock Photos Vectors Adobe Stock




Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And Physiology I
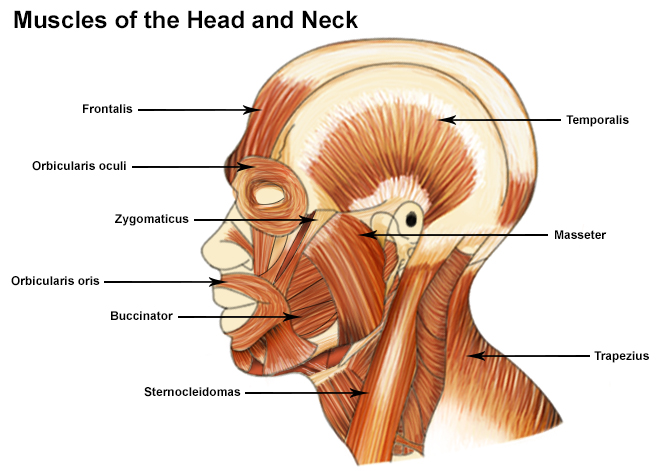



Seer Training Muscles Of The Head And Neck
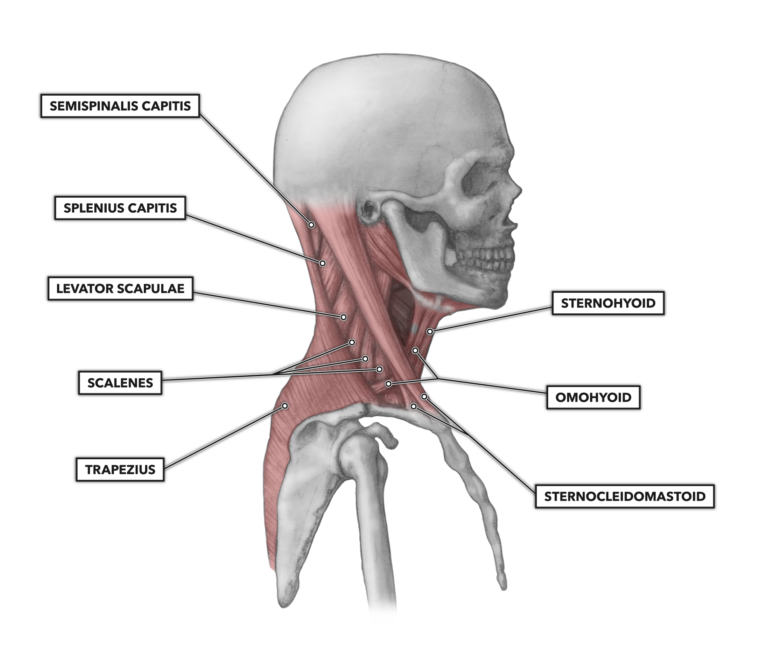



Crossfit Cervical Muscles Part 1
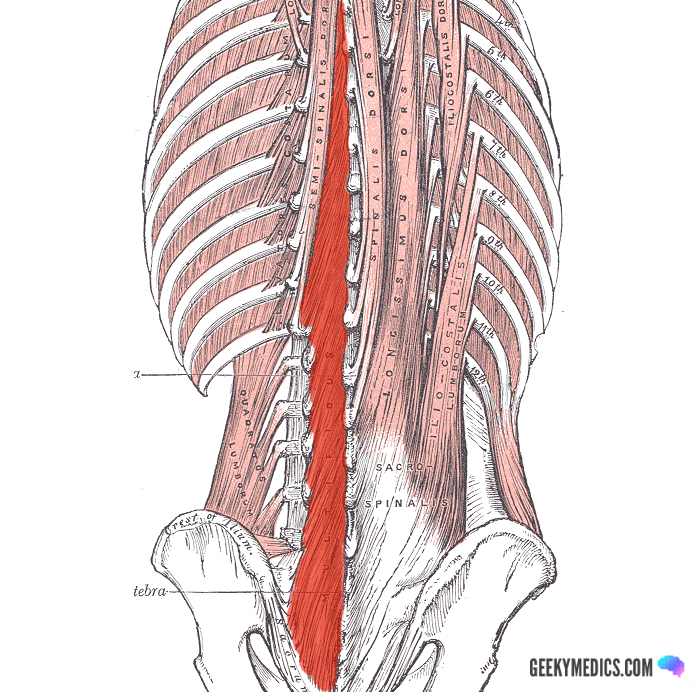



Deep Back Muscles Anatomy Geeky Medics
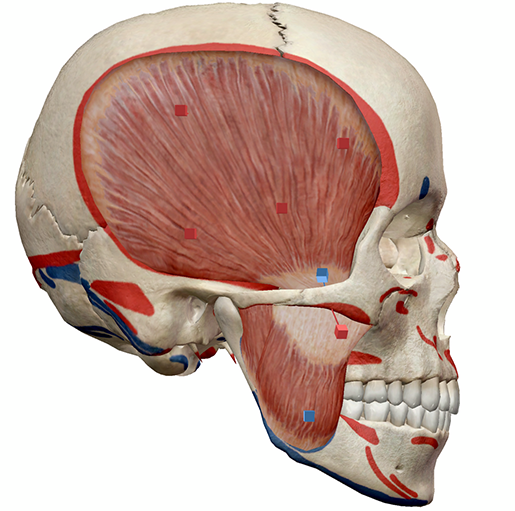



Learn Muscle Anatomy Muscles Of Mastication
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/14074/Back_muscles.png)



Back Muscles Anatomy And Functions Kenhub
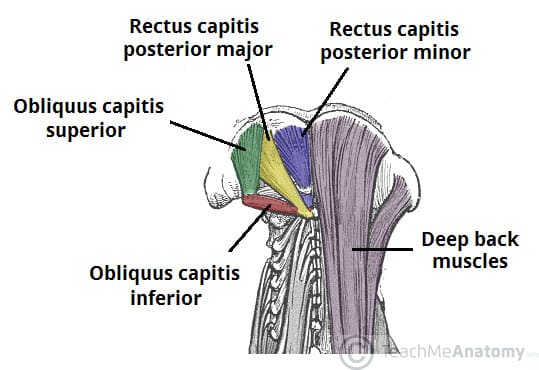



Suboccipital Muscles Attachments Actions Innervation Teachmeanatomy
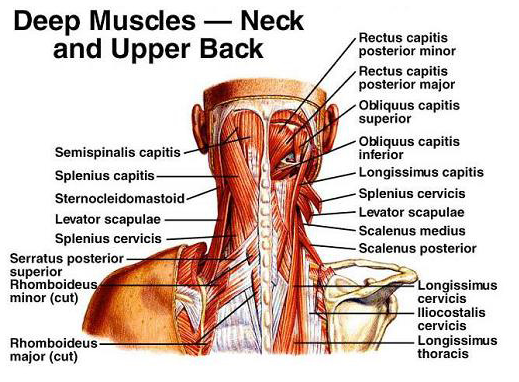



Cervical Motor Control Part 1 Clinical Anatomy Of Cervical Spine Rayner Smale
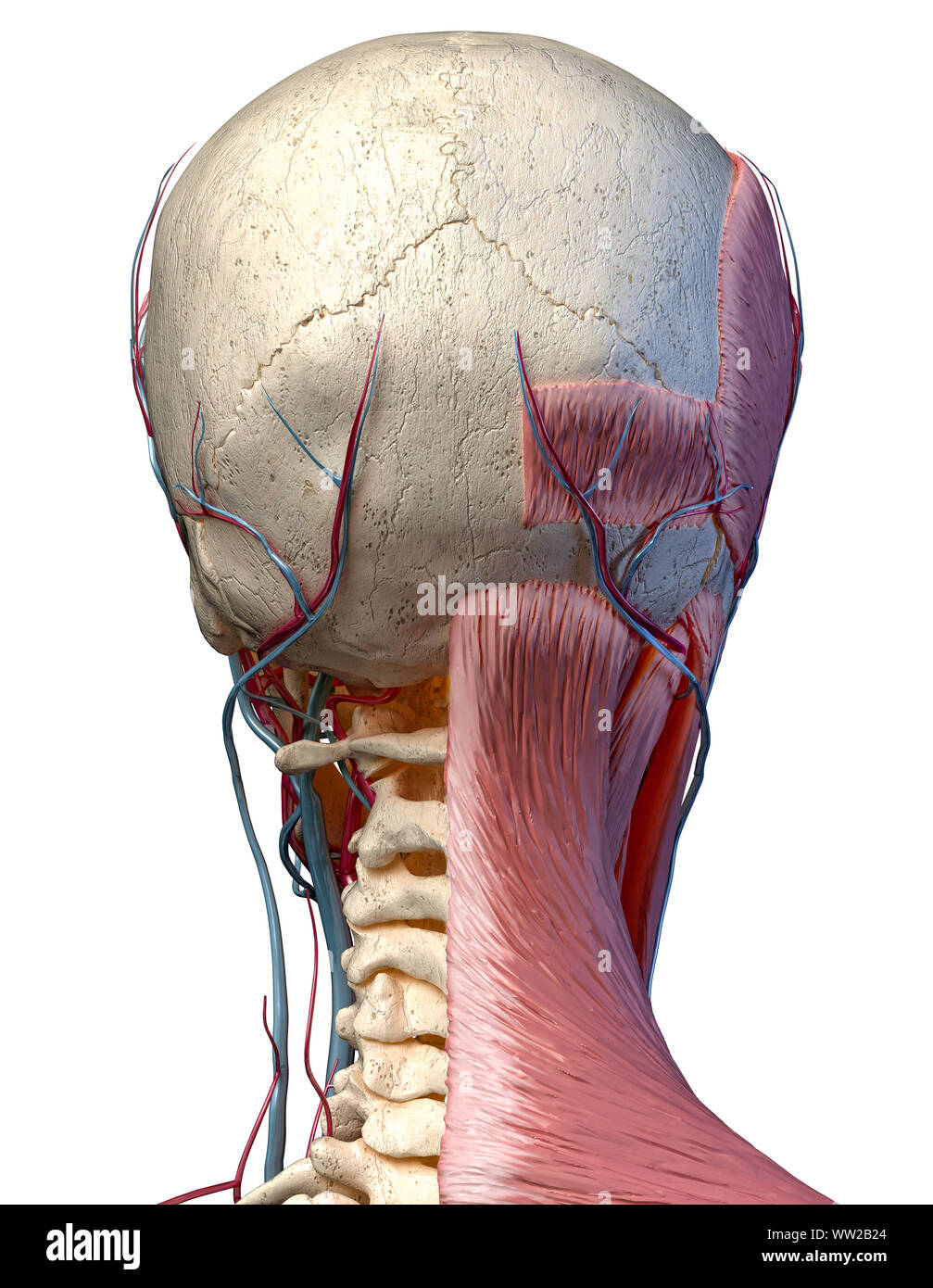



Human Anatomy 3d Illustration Of Head With Skull Blood Vessels And Muscles On White Background Rear View Stock Photo Alamy




Human Anatomy Showing Face Head Shoulders And Back Muscular Posters For The Wall Posters Medicals Organ Bone Myloview Com



1




Pin By Limclari On Anatomy Neck Muscle Anatomy Human Muscle Anatomy Anatomy
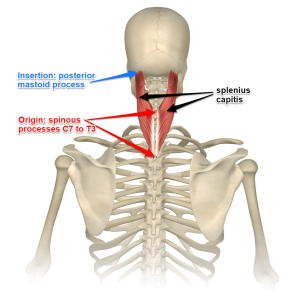



Understanding The Spinotransversales The Superficial Intrinsic Muscles Of The Back




Head And Neck Pain Back In The Game Physical Therapy




Massage For Neck Pain Headaches Suboccipitals



Physiotherapyinleeds Co Uk
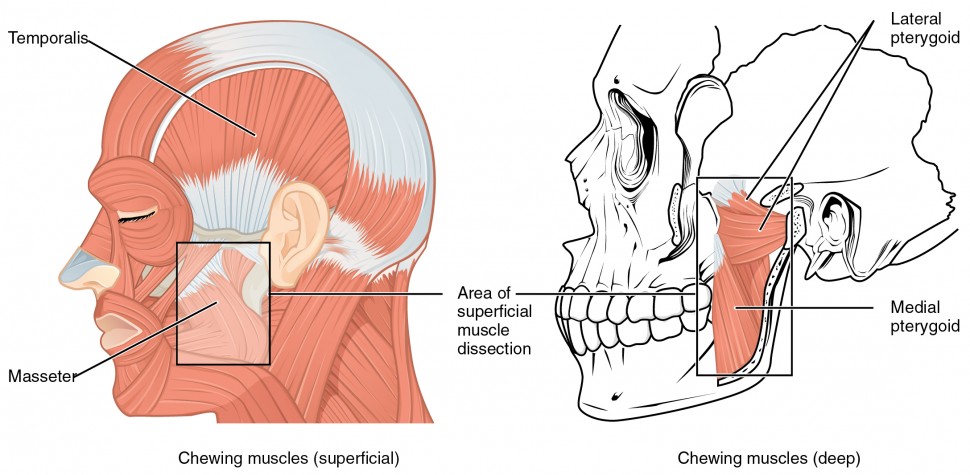



Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And Physiology I
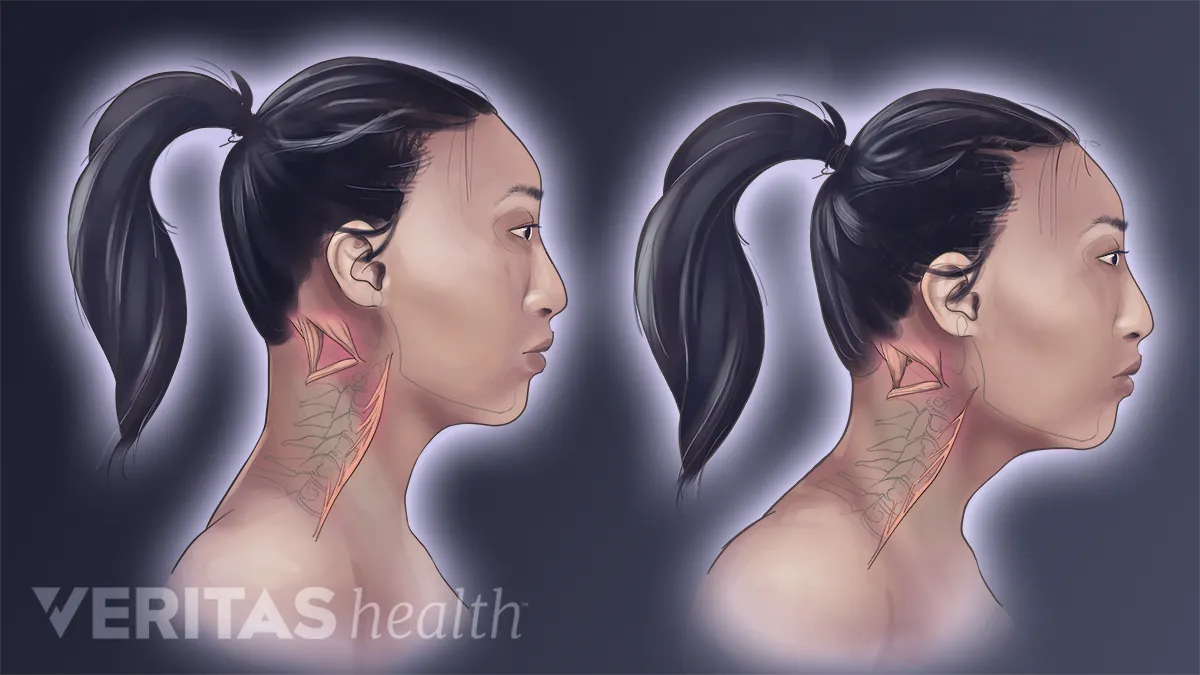



Forward Head Posture S Effect On Neck Muscles




Back Muscles Anatomy Of Upper Middle Lower Back Pain In Diagrams Goodpath




Drawings Muscular Anatomy Of The Back Stock Illustration Gg Gograph




Back Of Head Anatomy Muscles Manual




Muscles Of The Head Neck Anatomy Model Youtube



Muscle Anatomy




Anatomy Of Back Of Head Anatomy Drawing Diagram




3d Illustration Female Head Muscles Anatomy Stock Illustration
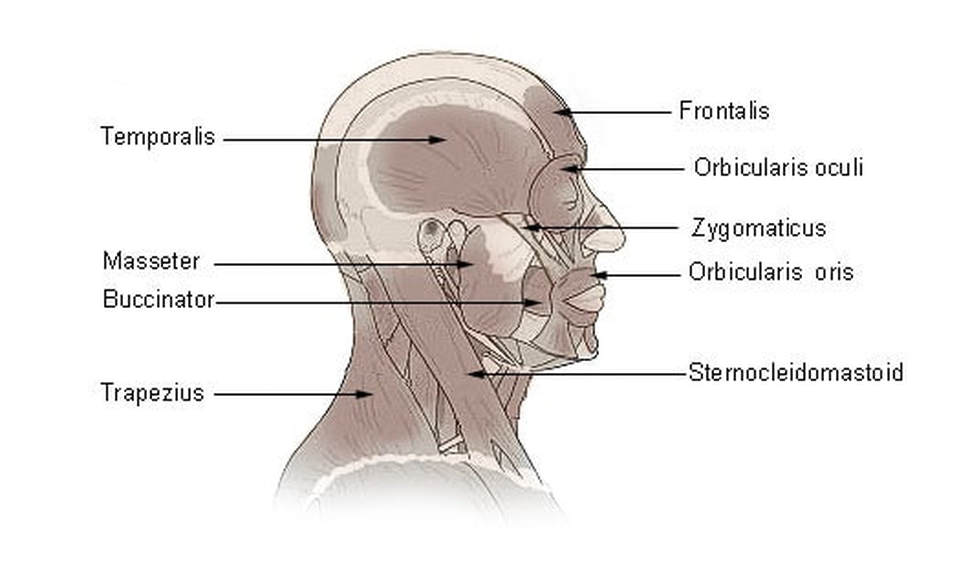



The Muscles Of The Head Trunk And Shoulders Scientist Cindy




Human Head Anatomy Back View Stock Photo By C Anatomyinsider




Human Anatomy Showing Face Head Shoulders And Back Stock Photo Download Image Now Istock




Muscles Of Trunk Back Stock Image C0 0430 Science Photo Library



Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy Physiology




Intrinsic Back Muscles Anatomy Of The Torso Medical Library
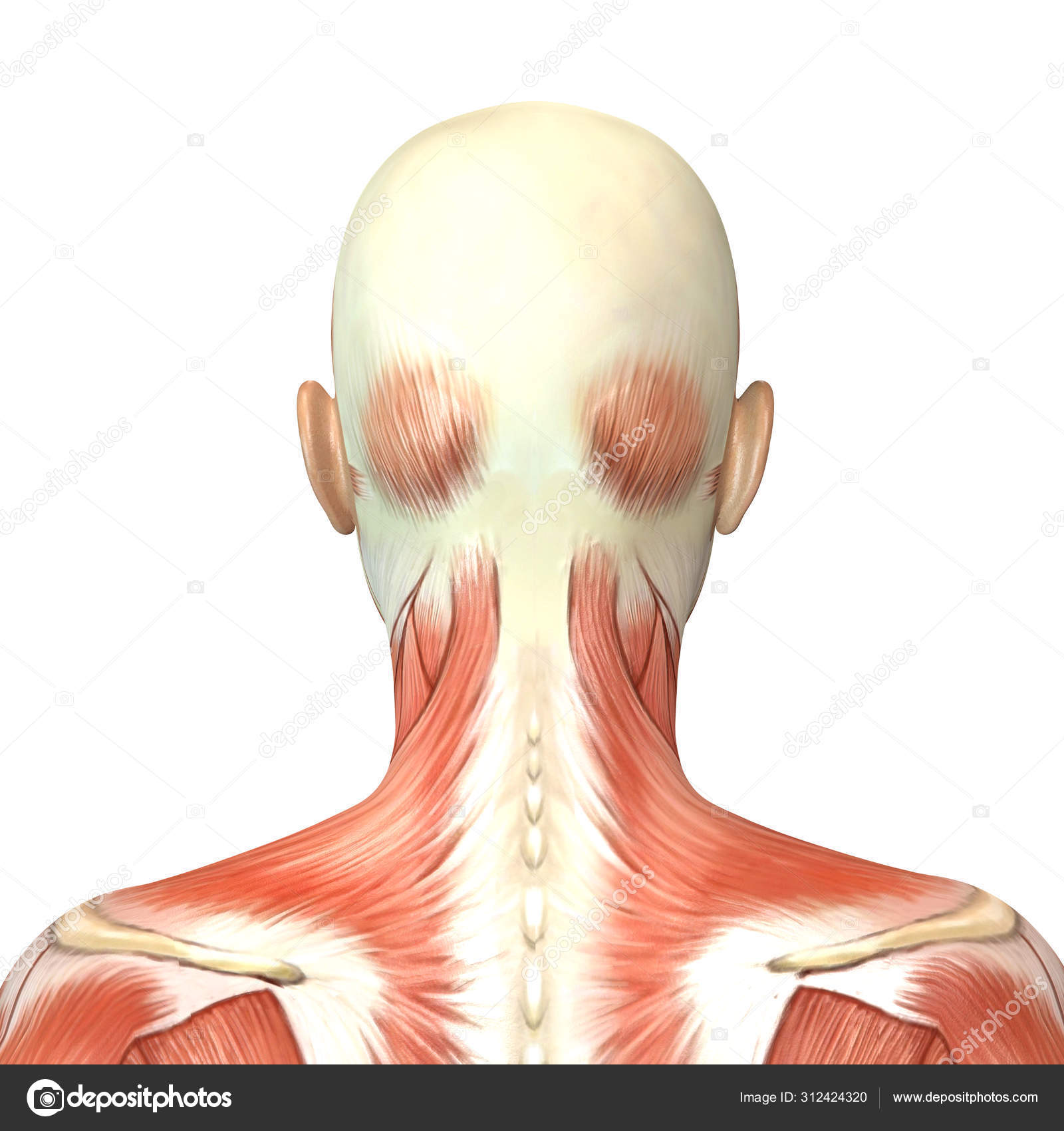



3d Illustration Of Female Head Muscles Anatomy Back View Stock Photo By C Deryadraws
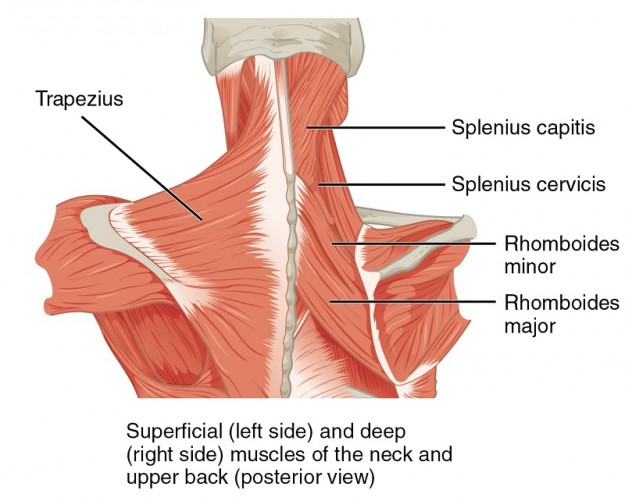



Intrinsic Back Muscles Anatomy Of The Torso Medical Library
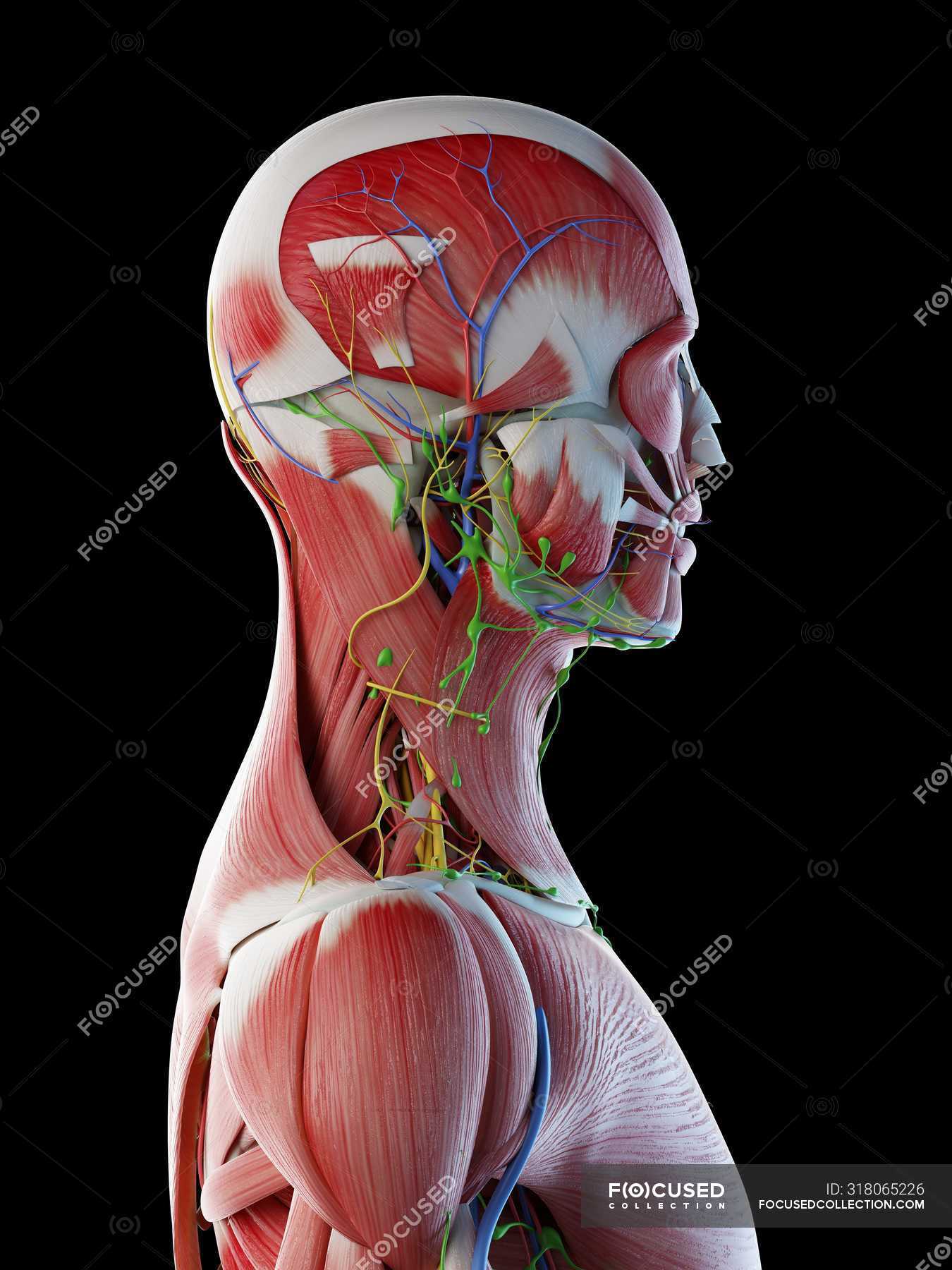



Male Anatomy Of Head Neck And Back With Musculature Computer Illustration Normal Transparent Stock Photo




Axial Muscles Of The Head Neck And Back Anatomy And Physiology I
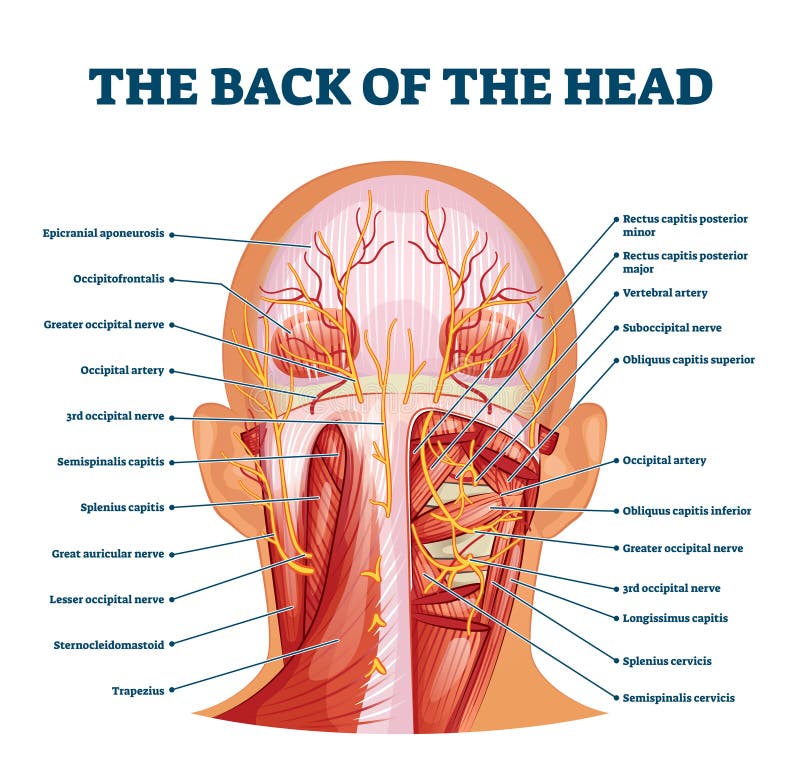



Back Of The Head Muscle Structure And Nerve System Diagram Stock Vector Illustration Of Labeled Muscle



1




Human Head Muscle Anatomy Stock Photos Page 1 Masterfile



Upper Back Pain Anatomy Of The Back The Pain Center Pain Management Care
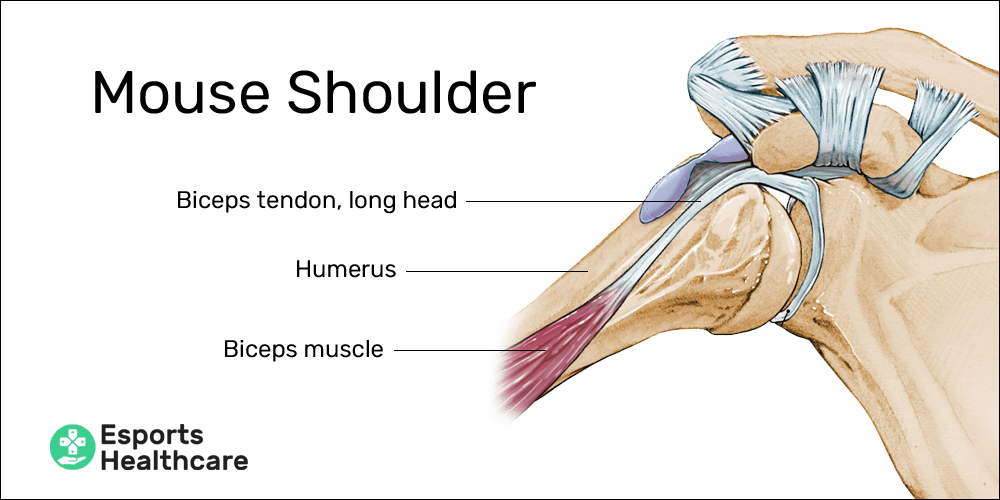



Mouse Shoulder A Painful Ailment For Pc Gamers Esports Healthcare
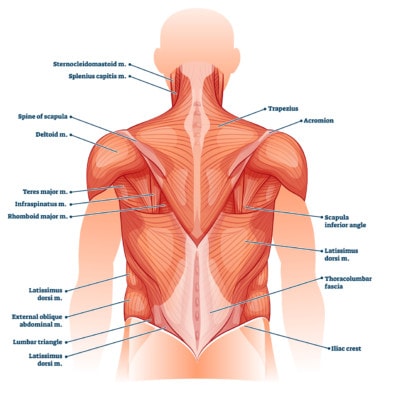



Your Back Problem May Be Destroying Back Muscles
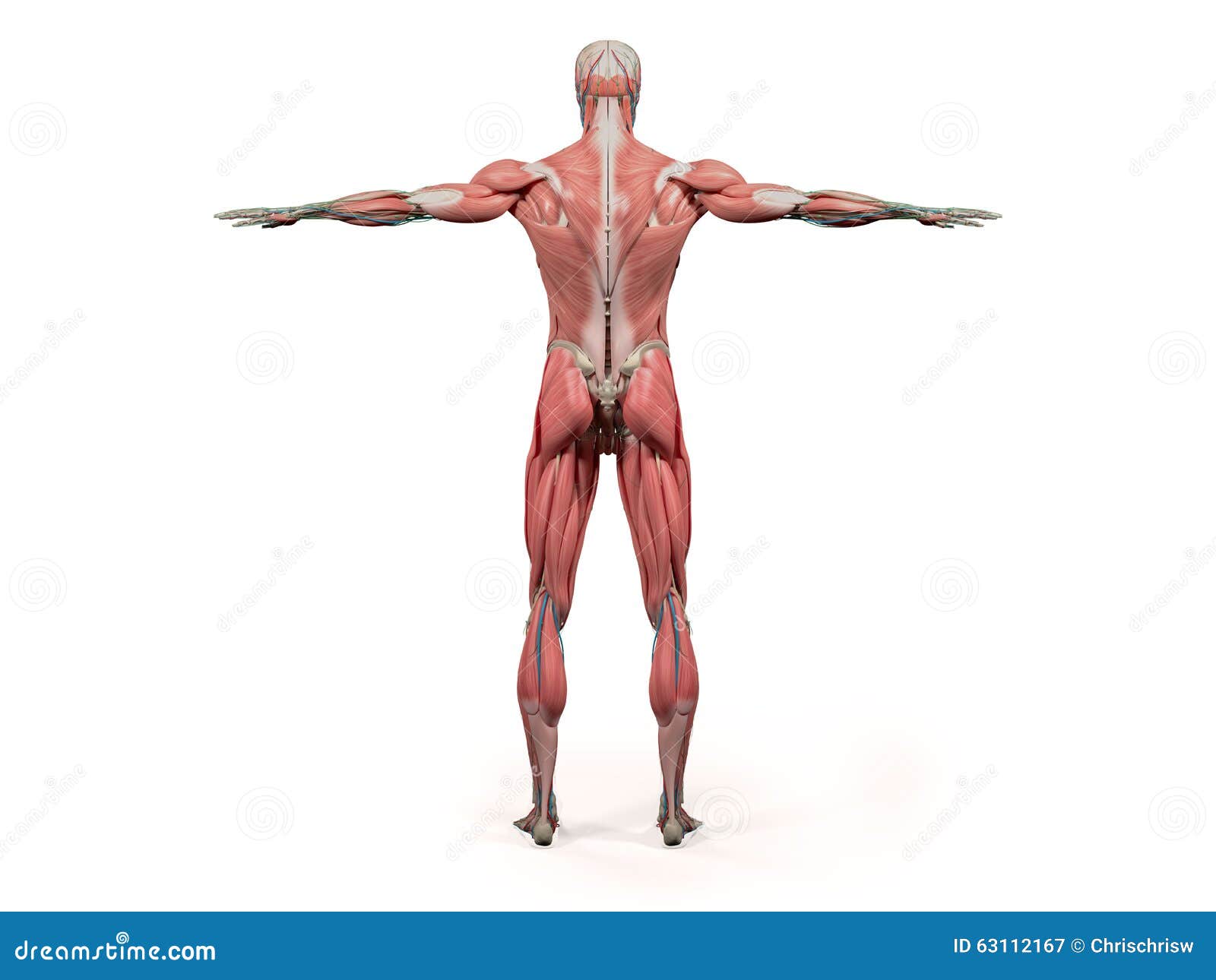



Back Head Anatomy Stock Illustrations 2 481 Back Head Anatomy Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




Occipital Neuralgia And Suboccipital Headache C2 Neuralgia Treatments Without Nerve Block Or Surgery Caring Medical Florida
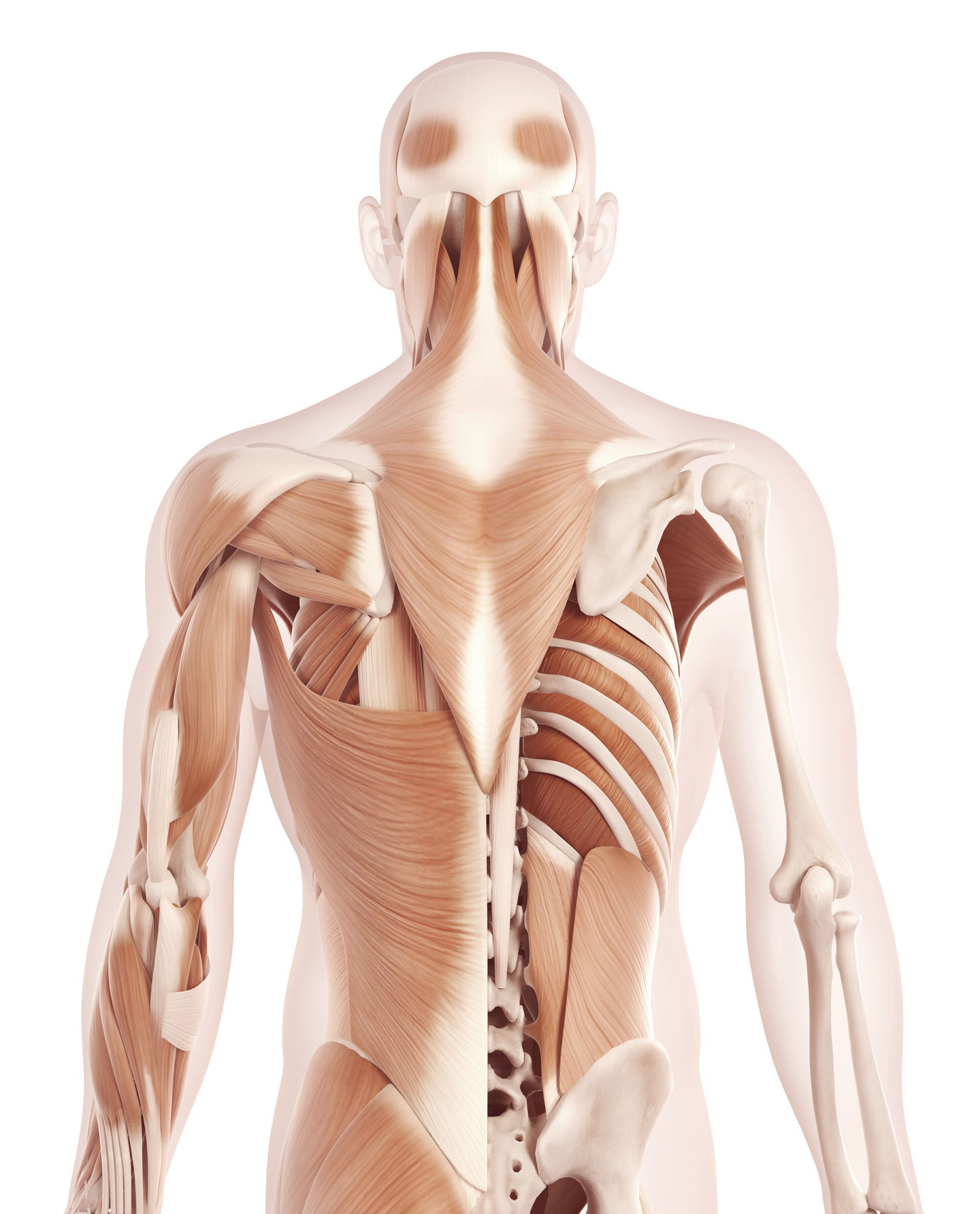



The Anatomy Of Your Tension Headache Somatic Movement Center



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿