Disagreements between former Yugoslavs over their nineteenthcentury history, although deep, pale into insignificance when compared to different interpretations of more contentious subjects, such as the Second World War in Yugoslavia () Because the wars of the 1990s have finished so recently it is too early to predict how the former At this point in our river cruise we are entering the former Yugoslavia It is extremely difficult to explain why this country broke up in the 1990s, so I am reprinting this article from fellow travel writer Rick Steves' website I think it will be helpful in understanding this part of the world For uptodate specifics, see the latest edition of the Rick Steves' Eastern Europe guidebook Seven countries make up former Yugoslavian republics, including Bosnia and Herzegovnia, Montenegro, Croatia, Macedonia, Slovenia, Serbia, and Kosovo Most of these republics became independent nations after ethnic cleansing and civil war swept through the former Yugoslavia during the early 1990s
Full Article The Eu S Stability Democracy Dilemma In The Context Of The Problematic Accession Of The Western Balkan States
The former yugoslavia became the most troubled region of europe in the 1990s because
The former yugoslavia became the most troubled region of europe in the 1990s because-Answer (1 of 10) It was more prosperous, compared to countries under Soviet occupation and control in Eastern Europe or an independent communist state like Albania I seriously don't think it was more prosperous than China or the Soviet Union itself I Eastern Europe was the most troubled region in Europe in the 90's Wiki User ∙ 1951 This answer is



2
The former Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY) was important subject of the international community Internally this federation was composed by six republics, and two autonomous provinces It was country located on the historically very important geopolitical in the Balkans region Yugoslavia dissolved in aAs part of former Yugoslavia and nonmembers of the Eastern Bloc, Slovenia and Montenegro enjoyed a special status and relationships with the European Communities (EC)The 1990s were a bloody period for the region as the former Yugoslav republics fought each other in what became known as the Yugoslav Wars The conflict gradually came to an end by the late 1990s, which also sparked democratic reforms in the FRY The nonSlavic region of Kosovo became an equal republic by 00, followed by Vojvodina
Asked in Political Science by Cookie a Bosnia b Macedonia c Serbia d Kosovo internationalrelations; The breakup of the Former Yugoslavia in the beginning of the 1990s continued breathing life into the maritime interception model that was set up by the MIF While Yugoslavia was falling apart, in 1991, the UNSC adopted SC Res 713 (1991) under Article 41, establishing an arms embargo The adoption of SC James Baker's visit to Yugoslavia in June 1991 was seen very differently by the various ethnicities within the former Yugoslavia It was important to the Slovenes and the Croats, for example, that they become members of the European Community as soon as possible as Slovenes and as Croats, not as Yugoslavs
The former Yugoslavia was situated in the central, northern, northwest, and western parts of the Balkan peninsula Among the geographical wholes in Europe, the Balkan peninsula has the most heterogeneous structure from the physicalgeographical, social geographical or any other aspect Under Josip Broz – Tito's brand of communism, the citizens of the former Yugoslavia were able to enjoy many more freedoms than their communist brethren in the Soviet Union One of the most impactful freedoms was religion Religious education and the production of religious literature was permitted again Yugoslavia 1918 03 By Tim Judah Last updated In Yugoslavia, what began as a noble idea ended in war, destruction and poverty As the remnant of the old Yugoslavia legislates
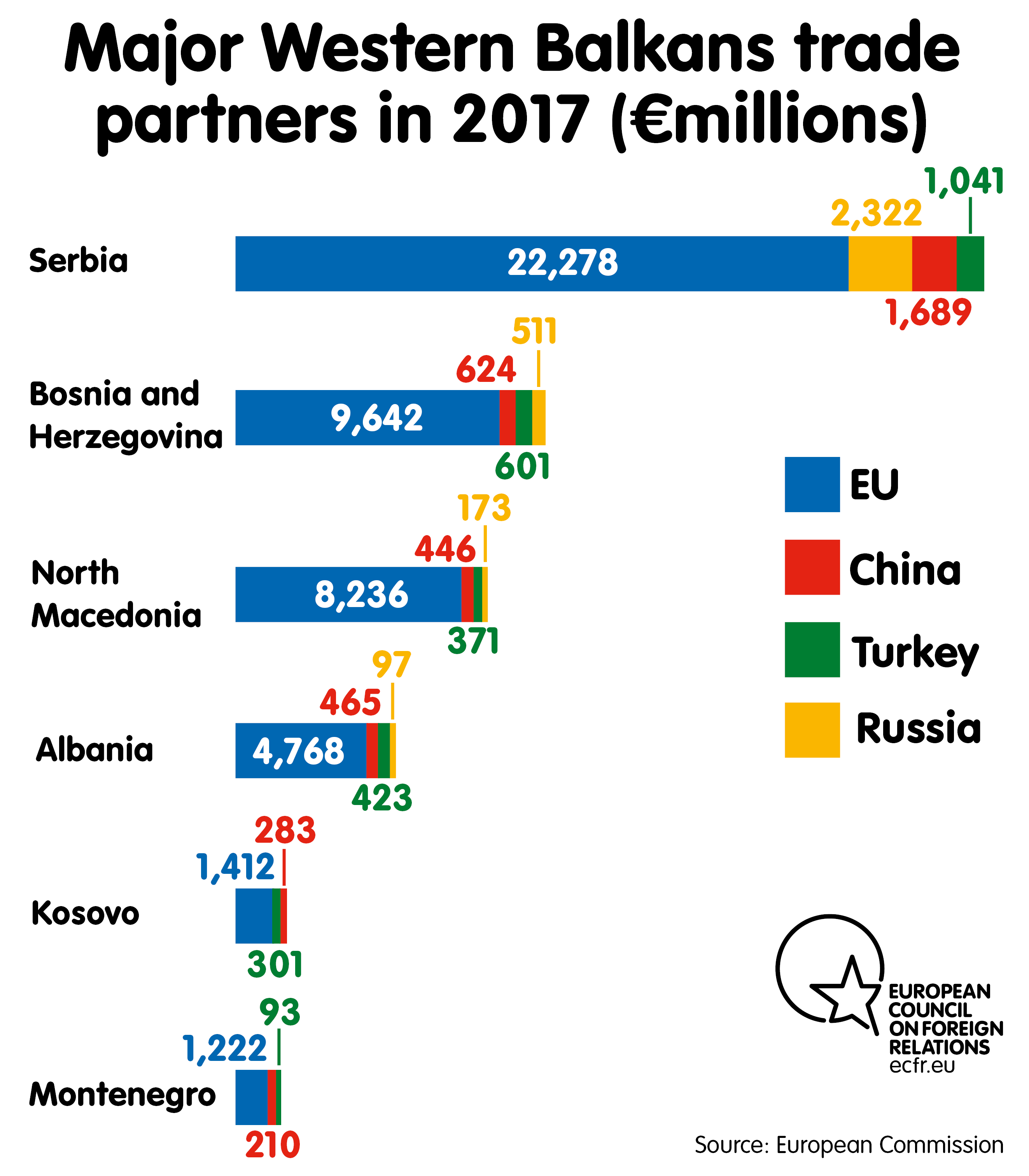



From Myth To Reality How To Understand Turkey S Role In The Western Balkans European Council On Foreign Relations



2
Answers to the most important questions 1 What conflicts were fought in the Balkans in the 1990s?Yugoslavia, former country that existed in the westcentral part of the Balkan Peninsula from 1929 until 03 It included the current countries of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, Slovenia, and the partially recognized country of Kosovo Learn more about Yugoslavia in this articleAnswer (1 of 6) A, thanks Slobodan What scenario would envelope if Yugoslavia joined the European Union at the beginning of the 1990s?



Full Article Lost In Transition The Liberal International Order In Eastern Europe And The South Caucasus



2
Yugoslavia and its history are often in the news yet poorly understood Traversing the politics, economics, demography, and culture of the former Yugoslavia, John B Allcock examines and makes sense of the region's troubled past and troubling present Explaining Yugoslavia (Paperback) Walmartcom Explaining Yugoslavia Yugoslavia came into existence as a result of World War I In 1914 only Serbia (which included presentday North Macedonia and Kosovo) and Montenegro were independent states;War Europe, in a region in which Western Slavic, Eastern Slavic, and Turkish cultures, Catholicism, Eastern Orthodoxy, and Islam all converge in a delicate balance Failure to contain Serbian aggression endangers regional stability and threatens a wider regional conflict A Former Yugoslavia As a Precedent For Regional Instability




Chapter 4 Right To Education In Revolution Of The Right To Education




Hieu 2 Chapter 33 Quiz Docx Hieu 2 Chapter 33 Quiz During The Decade Since 04 Africa Has Experienced A An Increase In The Death Rate Caused By Course Hero
Yugoslavia became the most troubled of former Eastern European communist countries because of all of the following EXCEPT asked in History by Amuneet a It was a multiethnic state created after World War One b It became embroiled in a war with CzechoslovakiaThe unraveling of former Yugoslavia brought with it a series of wars, mainly the war in CroatiaThen it'd mean that Slovenes, Slavomacedonians, or at least Croats, Serbs, and Muslims of Yugoslavia (aka



2




Introduction In Defending Eastern Europe
A) It is roughly twothirds of the United States B) It is about the size of the state of Texas C) It is the same size as the United States D) It is equal in size to the continental United States plus Alaska and HawaiiYugoslavia Twelve years ago, when I came to the United States, I had a country Today I do not What has been destroyed in the former Yugoslavia were not just cities and villages, but the concept of an integrated and ethnically diverse society In their desire to create homogeneous regions, nationalist groups have driven out, Former Yugoslavia 101 The Balkans Breakup If you're confused about how the former Yugoslavia dissolved after the fall of communism, you're not alone The country was melded together after World



2



2
YUGOSLAVIA 30 YEARS ON Scaling back the state The exYugoslav states have gone their separate ways but one thing they still have in common is the widespread and persistent belief of many of their citizens in the benefits of state involvement in the economy This was reinforced by the coronacrisis that saw the role of the state increase, butAlthough the 1990s are far gone the residues of their troubled past still linger The disintegration of former Yugoslavia and its aftermath had left behind economic, political and social carnage The international community headed by France and the United States intervened through the establishment of an ad hoc tribunal After reminding us that "For the World War II generation in eastern Europe, communism was the 'god that failed'", Feffer writes that "For the current generation in




Breakup Of Yugoslavia Wikipedia



2
Ch 8 GEOG 161 How does Europe compare in size (area) to the United States?The International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia (ICTY) was formally established by Resolution 7 of the United Nations Security Council on The establishment of UN Safe Areas is considered one of the most controversial decisions of the United Nations, due to uncertainty about how UN member states could protect what had become a wartorn, unstable The trouble with Belgrade's street names 5 Min Read Nikola Đorđević Belgrade's city government is pushing forward with its policy of renaming Yugoslavera streets With other capitals in the former Yugoslavia having done so in the 1990s, Yugoslavian multiculturalism seems headed for the dustbin of history Osječka




The Rise And Fall Of Market Socialism In Yugoslavia Doc Research Institute




Macedonia Naming Dispute Wikipedia
The Breakup of Yugoslavia, 1990–1992 Issued on , National Intelligence Estimate (NIE) 15–90 presented a dire warning to the US policy community Yugoslavia will cease to function as a federal state within a year, and will probably dissolve within two Distinguished sociologist Kai Erikson described his many journeys to the town of Pakrac, in the former Yugoslavia, beginning during the war in 1992, and the interviews he conducted with current and former residents of the townWhat region of the former Yugoslavia became the scene of NATO intervention in 1999?
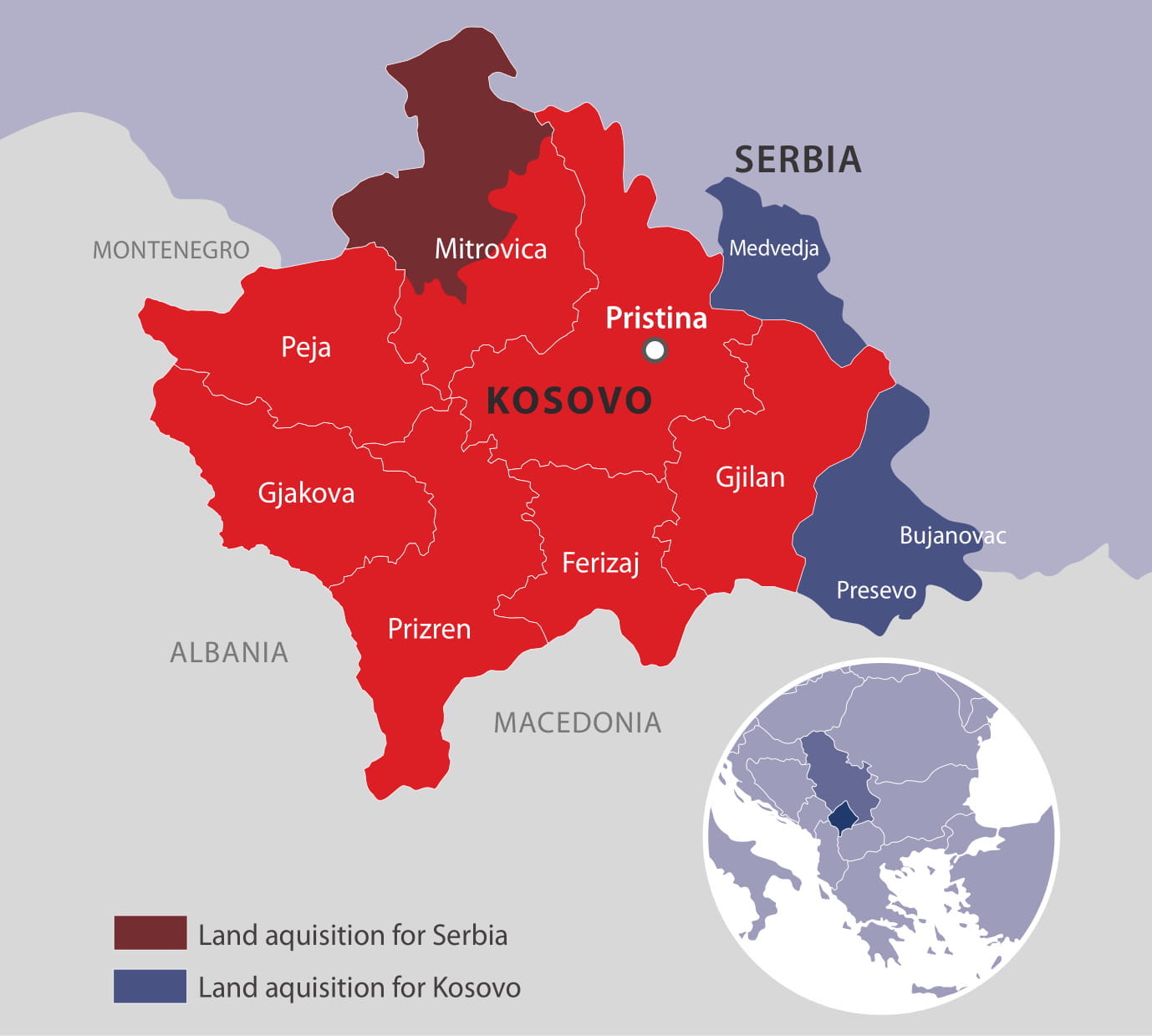



The Proposed Territorial Exchange Between Serbia And Kosovo Commentaries Aleksander Zdravkovski Sabrina P Ramet Insight Turkey




Pdf The Yugoslav Successor States From Self Management Socialism To Political Capitalism
Pavlicevic declined to make a score prediction for a 1990 Yugoslavia vs 19 Yugoslavia tilt but said he thought the vintage Yugoslavia side would win against Yugoslavia 19 He also noted that Greece, runnerup to Spain at the 06 FIBA World Championship, learned by watching the former Yugoslavia playEleven years later, it was named "Yugoslavia" A journey through a torn region Seen from above, Serbia is paradise Belgrade, the capital, is idyllically situated at the confluence of the Danube and



2



2
0 Answers 0 votes answered by nanx1998The breakup of Yugoslavia occurred as a result of a series of political upheavals and conflicts during the early 1990s After a period of political and economic crisis in the 1980s, constituent republics of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia split apart, but the unresolved issues caused bitter interethnic Yugoslav warsThe wars primarily affected Bosnia and Herzegovina,The 1990s Ethnic Conflict in Former Yugoslavia Wars, conflicts, reformations were most of the issues in the 19 th century The desire to seek for freedom, equality, and justice In most of the wars and conflicts around the world in the 19 th century was somehow based on religion, freedom, injustice, inequality and properties




A Journey Through The Troubled Former Yugoslavia They Will Never Stop Hating Us Der Spiegel




Breakup Of Yugoslavia Wikipedia
Eastern Europe fell under the influence of the Soviet Union, and the region was separated from the West When the Soviet Union collapsed in 1991, all the Soviet Republics bordering Eastern Europe declared independence from Russia and united with the rest of Europe The transition Eastern Europe has experienced in the last few decades has notThe Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, commonly referred to as SFR Yugoslavia or simply Yugoslavia, was a country in Southeast and Central Europe that existed from its foundation in the aftermath of World War II until its dissolution in 1992 amid the Yugoslav Wars Covering an area of 255,804 km 2 (98,766 sq mi), the SFRY bordered theEurope Yugoslavia, 1918 Birth of a dead state Exactly 100 years ago, the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes proclaimed its union;
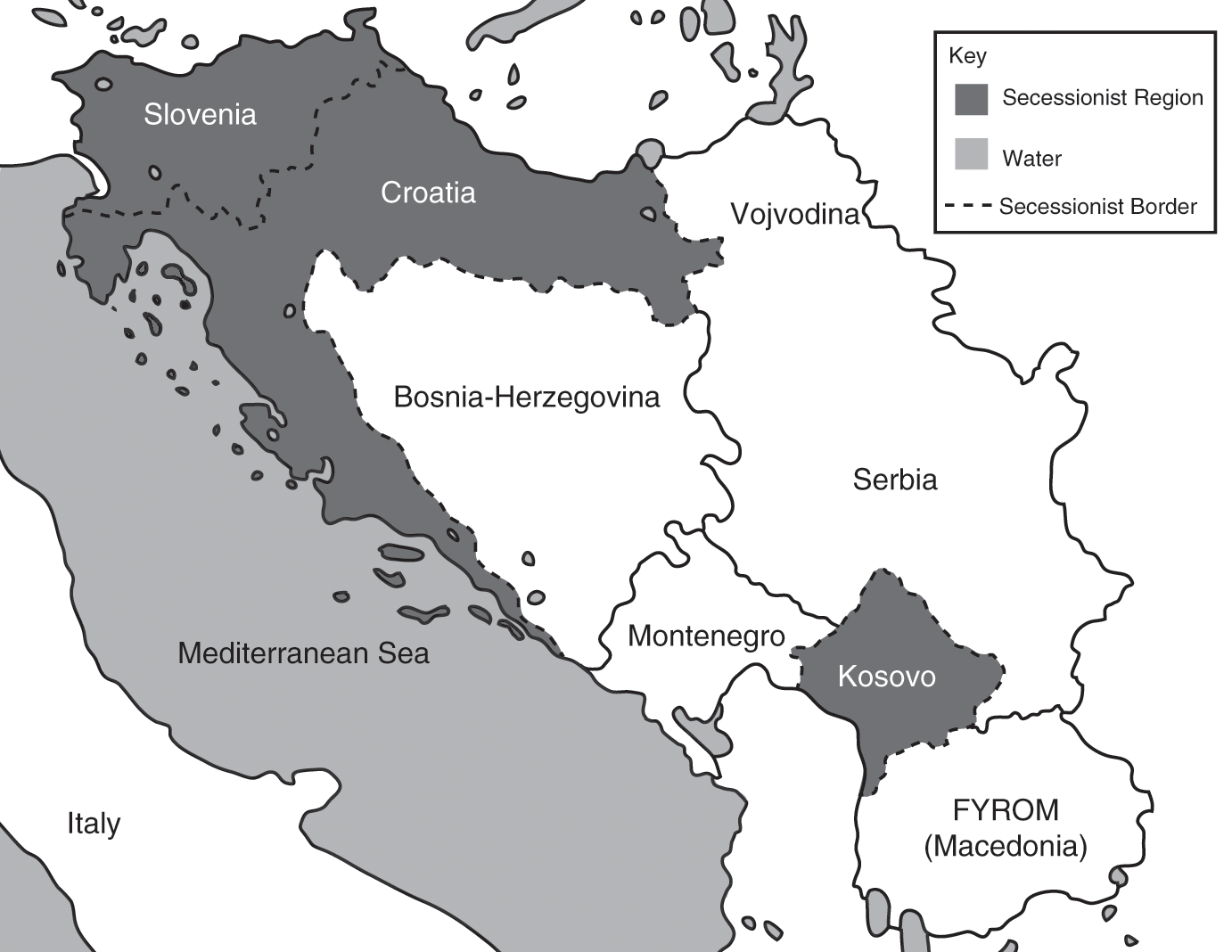



International Responses To Secession In Yugoslavia 19 11 Chapter 5 Power Politics And State Formation In The Twentieth Century




The Rise And Fall Of Market Socialism In Yugoslavia Doc Research Institute
Croatia, Slovenia, and Bosnia and Herzegovina belonged to the AustroHungarian Monarchy (The earlier histories of Yugoslavia's six component republics are treated in more detail in theirBecause of this timing, the first histories of the Yugoslav wars did not integrate Kosovo well mid1990s works could allude to Kosovo as a potential future zone of instability and a source of evidence about Milošević's regime, but could not know the outcome, and some so heavily emphasized the Serb/Croat relationship that Kosovo remained sidelined




International Responses To Secession In Yugoslavia 19 11 Chapter 5 Power Politics And State Formation In The Twentieth Century




Macedonia Naming Dispute Wikipedia



2



3



Full Article Between Europe And The Past Collective Identification And Diffusion Of Student Contention To And From Serbia




International Responses To Secession In Yugoslavia 19 11 Chapter 5 Power Politics And State Formation In The Twentieth Century




Mise En Page 1




A Journey Through The Troubled Former Yugoslavia They Will Never Stop Hating Us Der Spiegel



2
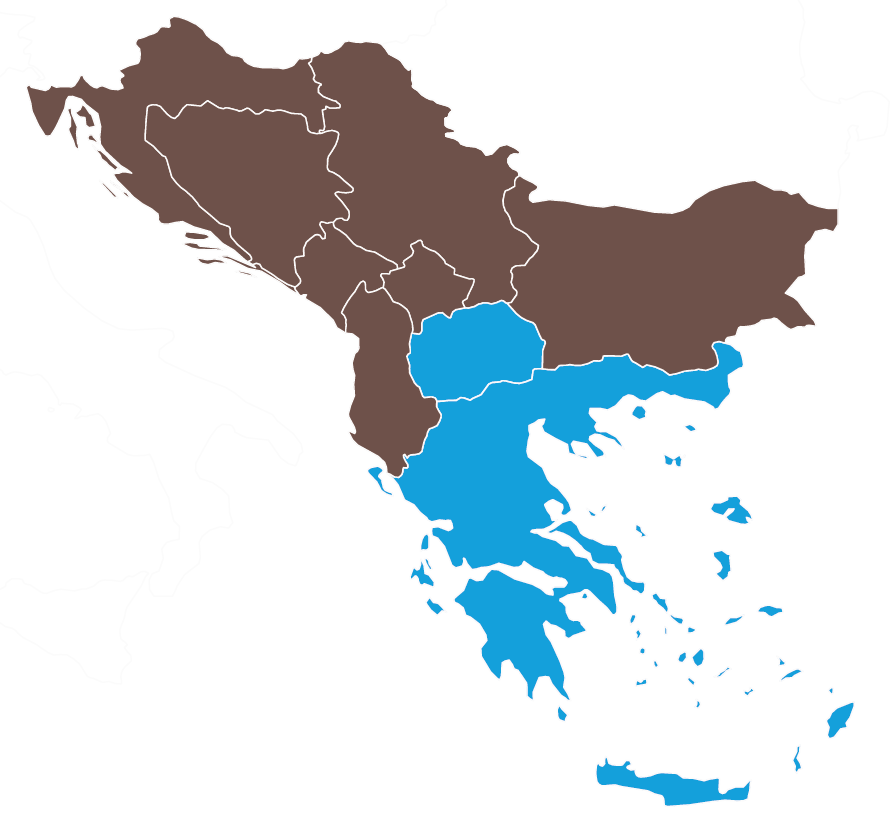



The Power Of Perspective Why Eu Membership Still Matters In The Western Balkans European Council On Foreign Relations



2



Documents1 Worldbank Org
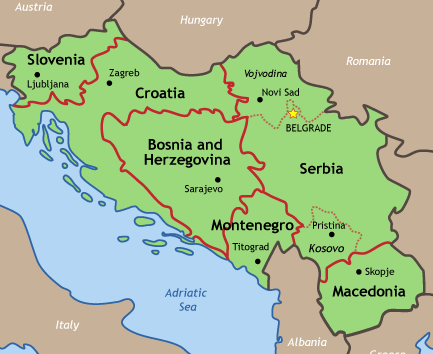



The Conflicts International Criminal Tribunal For The Former Yugoslavia




The Rise And Fall Of Market Socialism In Yugoslavia Doc Research Institute



1




Pdf Post Socialist Political Graffiti In The Balkans And Central Europe




Hieu 2 Chapter 33 Quiz Docx Hieu 2 Chapter 33 Quiz During The Decade Since 04 Africa Has Experienced A An Increase In The Death Rate Caused By Course Hero




The Rise And Fall Of Market Socialism In Yugoslavia Doc Research Institute




Serbia And Montenegro Wikiwand




Pdf Smuggling In Southeast Europe The Yugoslav Wars And The Development Of Regional Criminal Networks In The Balkans




The Rise And Fall Of Market Socialism In Yugoslavia Doc Research Institute



2




A Journey Through The Troubled Former Yugoslavia They Will Never Stop Hating Us Der Spiegel



Robert M Hayden S From Yugoslavia To The Western Balkans In Southeastern Europe Volume 38 Issue 2 3 14



Ifsh De



Cap Lmu De




Monthly Review The Dismantling Of Yugoslavia Part I




Chapter 9 Europolis From A Piratical Republic To A Collective Colony In The European Commission Of The Danube 1856 1948



Comparative Southeast European Studies Volume 69 Issue 1 In The Name Of The Daughter Anthropology Of Gender In Montenegro



A Troubled Partnership The Us And Europe In The Middle East Centre For European Reform
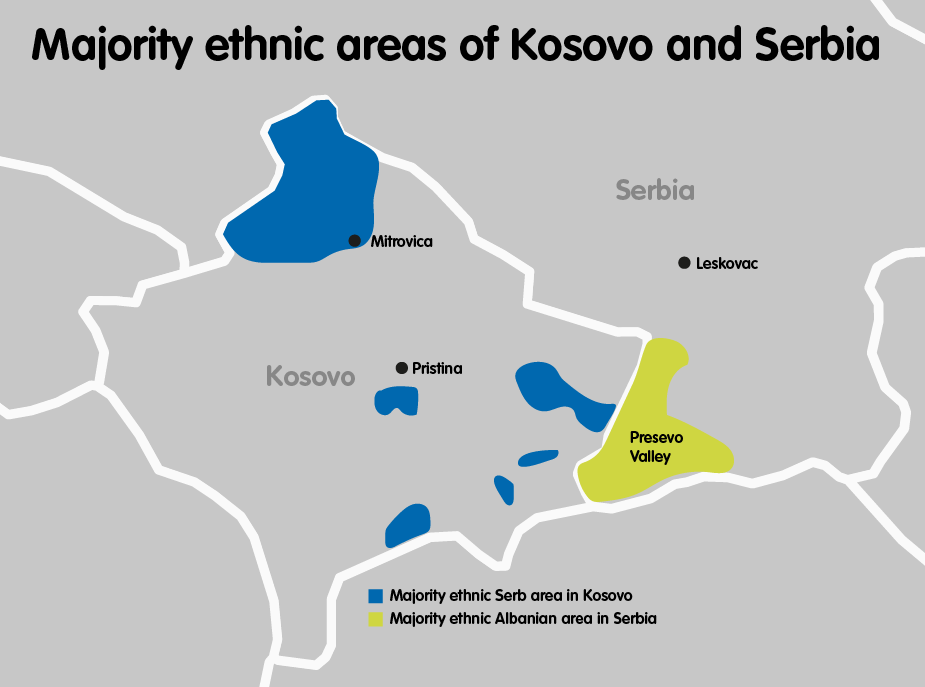



The Power Of Perspective Why Eu Membership Still Matters In The Western Balkans European Council On Foreign Relations



Jstor Org



Map




Pdf Croatia Europeanization Or Balkanization



Cadmus Eui Eu



Yugoslavia




Fdi Into Transition Economies Estrin 14 Economics Of Transition And Institutional Change Wiley Online Library




Balkan Wars Wikipedia




Semaphore Trouble In The Balkans The Royal Australian Navy In Yugoslavia Royal Australian Navy



Full Article The Eu S Stability Democracy Dilemma In The Context Of The Problematic Accession Of The Western Balkan States



2



2




The Power Of Perspective Why Eu Membership Still Matters In The Western Balkans European Council On Foreign Relations




219 Pdfs Review Articles In Yugoslavia




Miss Ex Yugoslavia Book By Sofija Stefanovic Official Publisher Page Simon Schuster



2




A Journey Through The Troubled Former Yugoslavia They Will Never Stop Hating Us Der Spiegel



Full Article Out Of Order The Us Alliance In Germany S Foreign And Security Policy




Russia S Game In The Balkans Carnegie Endowment For International Peace




Pdf Relationship With The European Union Slovenia And Montenegro Compared



2



2




Riassunto Buchanan Europe S Troubled Peace 1945 To The Present Docsity



2




Hieu 2 Chapter 33 Quiz Docx Hieu 2 Chapter 33 Quiz During The Decade Since 04 Africa Has Experienced A An Increase In The Death Rate Caused By Course Hero




Yugoslavia European Communities Relations Wikipedia




Fdi Into Transition Economies Estrin 14 Economics Of Transition And Institutional Change Wiley Online Library
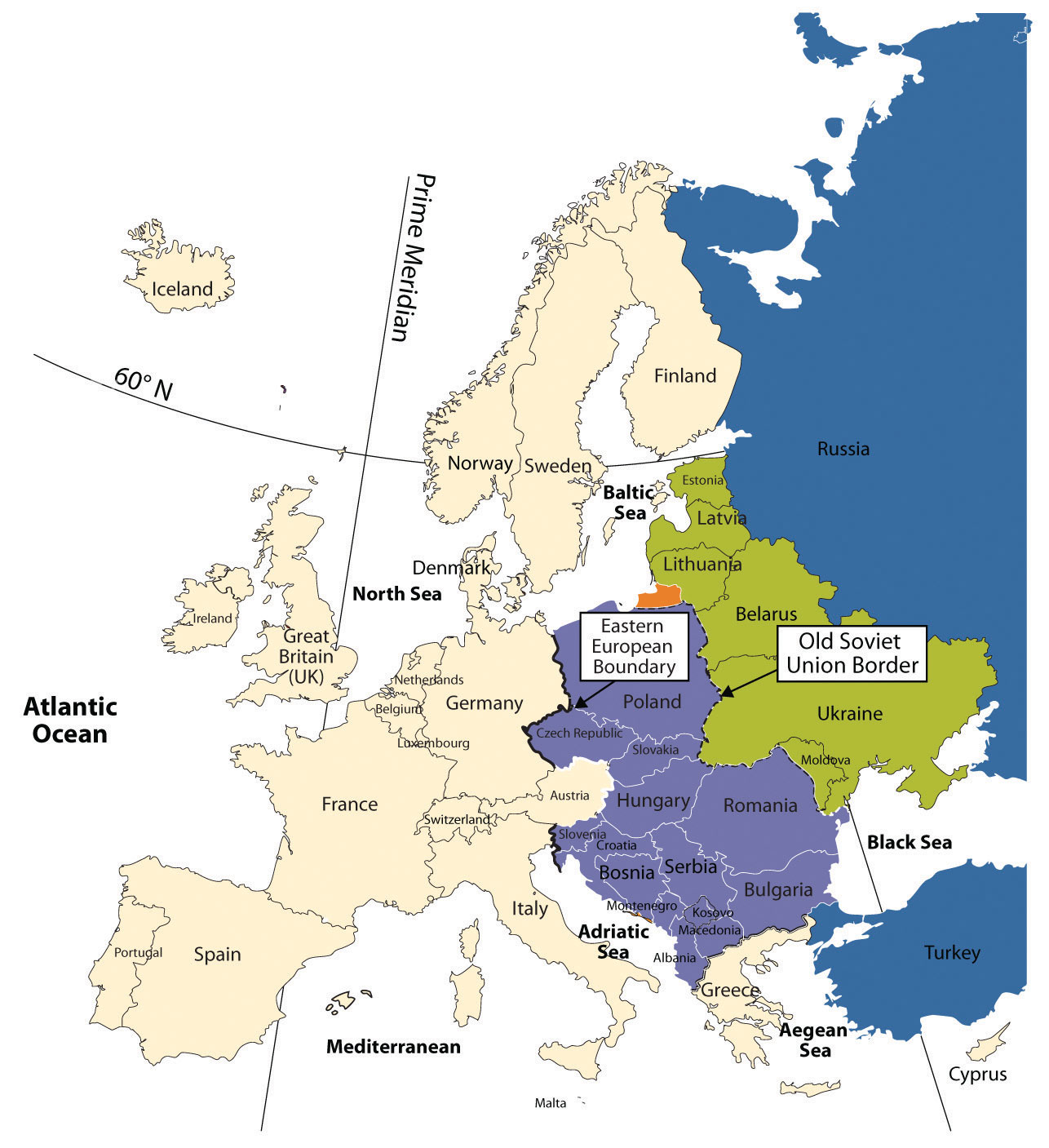



Eastern Europe




10 Conflicts To Watch In Crisis Group




The Rise And Fall Of Market Socialism In Yugoslavia Doc Research Institute



Full Article Caught Between Stability And Democracy In The Western Balkans A Comparative Analysis Of Paths Of Accession To The European Union



Introduction In Germany S Russia Problem
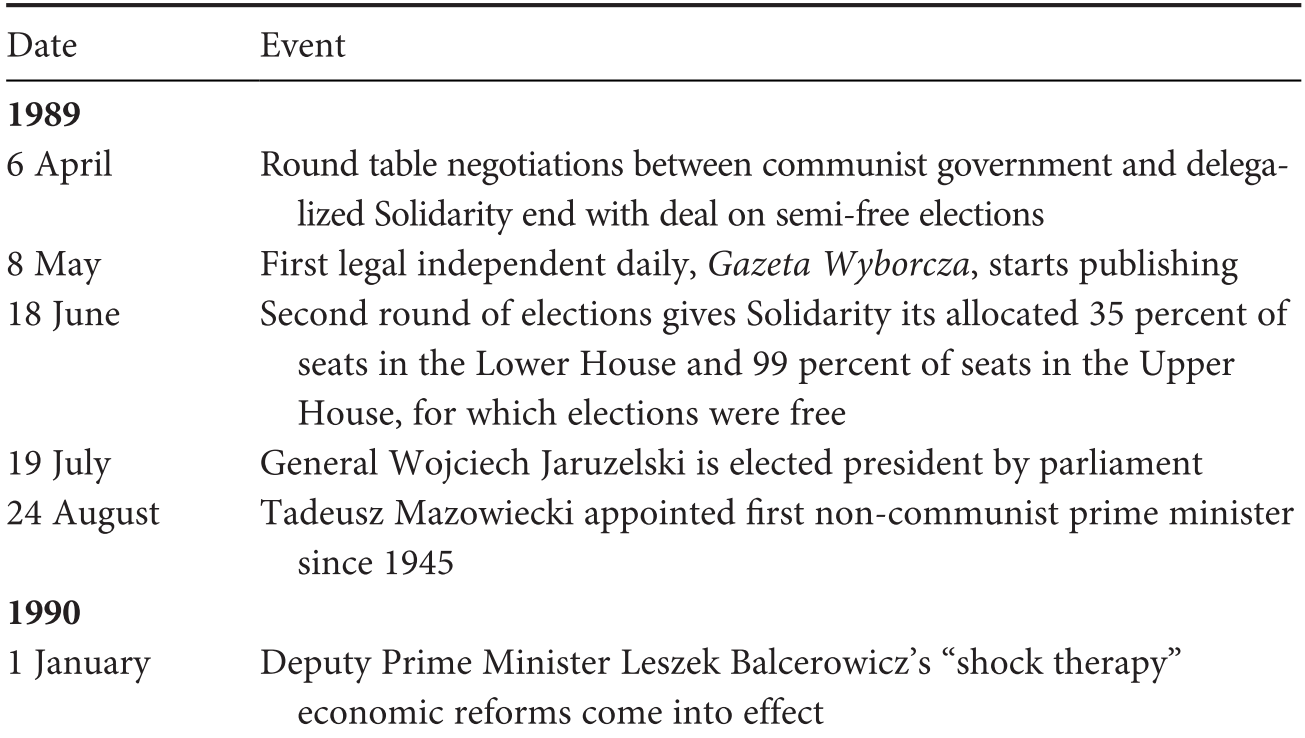



Central Europe Part Three Central And Southeast European Politics Since 19



2




Central Europe Part Three Central And Southeast European Politics Since 19




Pdf Europe S Troubled Region Economic Development Institutional Reform And Social Welfare In The Western Balkans
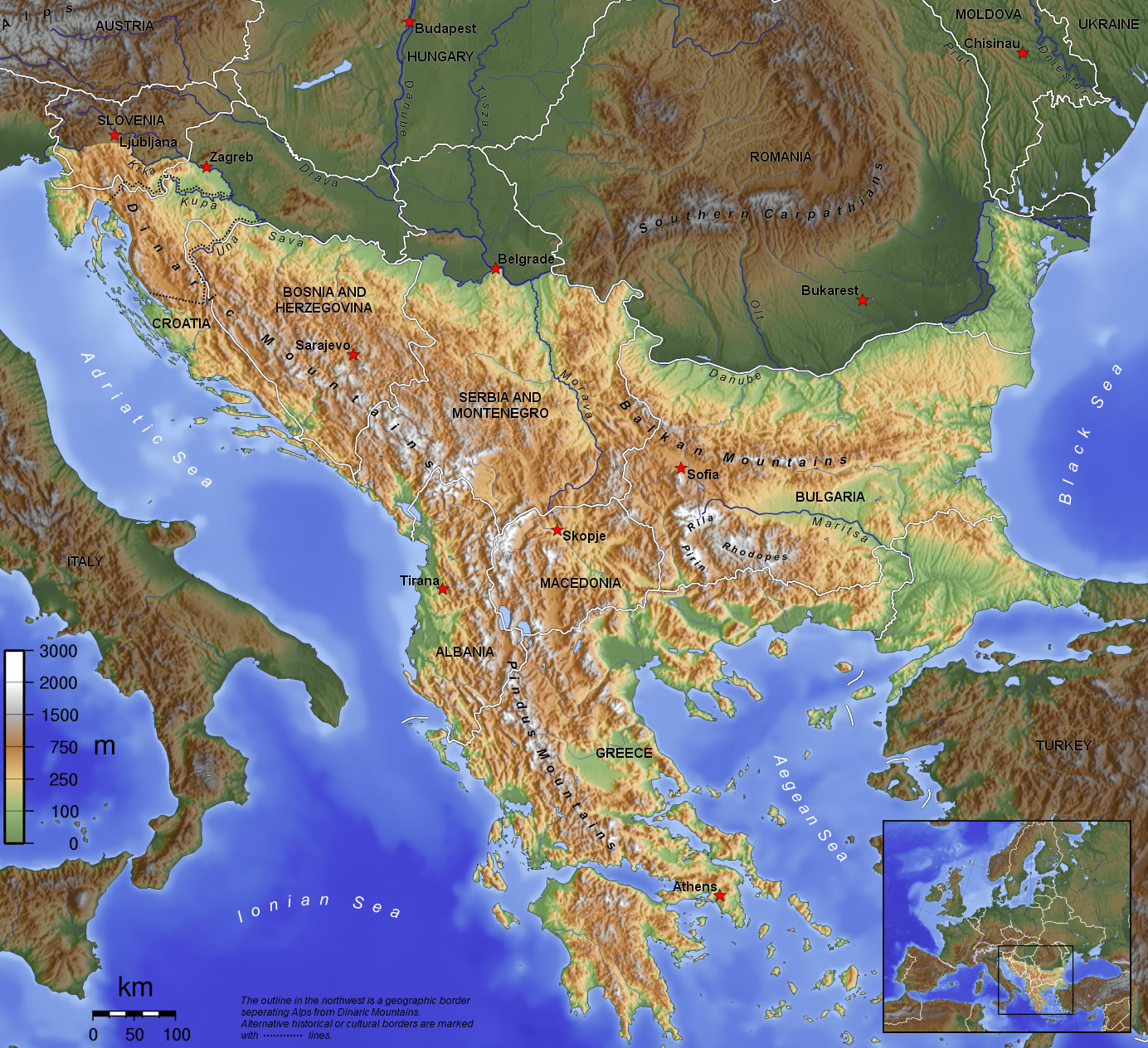



Balkans



Gppi



Db Thueringen De




A Journey Through The Troubled Former Yugoslavia They Will Never Stop Hating Us Der Spiegel



2




Fdi Into Transition Economies Estrin 14 Economics Of Transition And Institutional Change Wiley Online Library




The Impact Of The First World War And Its Implications For Europe Today Heinrich Boll Stiftung Brussels Office European Union



The Best And Worst Of Art In Central Europe In 19 Blok Magazine Blok Magazine




2 4 Eastern Europe World Regional Geography People Places And Globalization



2




Fdi Into Transition Economies Estrin 14 Economics Of Transition And Institutional Change Wiley Online Library



2




The Rise And Fall Of Market Socialism In Yugoslavia Doc Research Institute



2




A Journey Through The Troubled Former Yugoslavia They Will Never Stop Hating Us Der Spiegel



2



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿